Page 64 - ARNM-1-2
P. 64
Advances in Radiotherapy
& Nuclear Medicine A case of primary pulmonary FDCS
A B local recurrence and distant metastases were found
in this patient 1 year after surgery. These cases remind
us of the need to develop new treatment strategies and
further optimize and standardize the existing treatment
strategies for this disease to reduce the risk of post-
therapeutic recurrence and metastasis. Simultaneously,
considering that post-operative pathological results of
C D
lymph nodes (marked stations 2, 4, 7, and 11) showed
the presence of lung tissue, the absence of lymph nodes,
and tumor tissue, it is possible that the lymph nodes
(stations 2 and 4), which showed high uptake on PET
images (Figure 1A), were not removed for some specific
reasons. It cannot be ruled out that local recurrence
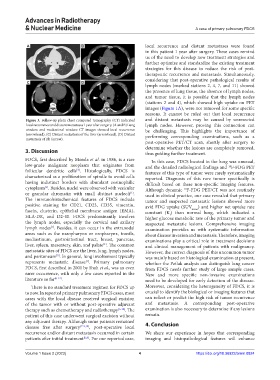
Figure 3. Follow-up plain chest computed tomography (CT) indicated and distant metastasis may be caused by unresected
local recurrence and distant metastases 1 year after surgery. (A and B) Lung lymph nodes. However, proving this connection can
window and mediastinal window CT images showed local recurrence be challenging. This highlights the importance of
(arrowhead). (C) Distant metastasis of the liver (arrowhead). (D) Distant performing corresponding examinations, such as a
metastasis of rib (arrow).
post-operative PET/CT scan, shortly after surgery to
3. Discussion determine whether the lesions are completely removed,
thus guiding further treatment.
FDCS, first described by Monda et al. in 1986, is a rare In this case, FDCS located in the lung was unusual,
low-grade malignant neoplasm that originates from and the detailed radiological findings and F-FDG PET
18
follicular dendritic cells . Histologically, FDCS is features of this type of tumor were rarely systematically
[4]
characterized as a proliferation of spindle to ovoid cells reported. Diagnosis of this rare tumor specifically is
having indistinct borders with abundant eosinophilic difficult based on these non-specific imaging features.
cytoplasm . Besides, nuclei were observed with vesicular Although dynamic F-FDG PET/CT was not routinely
[1]
18
or granular chromatin with small distinct nucleoli . used in clinical practice, our case revealed that primary
[1]
The immunohistochemical features of FDCS include tumor and suspected metastatic lesions showed more
positive staining for CD21, CD23, CD35, vimentin, avid FDG uptake (SUV ) and higher net uptake rate
mean
fascin, clusterin, epithelial membrane antigen (EMA), constant (K ) than normal lung, which indicated a
HLA-DR, and D2-40. FDCS predominantly involves higher glucose metabolic rate of the primary tumor and
i
the lymph nodes, especially the cervical and axillary suspected metastatic lesions. Comprehensive imaging
[1]
lymph nodes . Besides, it can occur in the extranodal examination provides us with systematic information
areas such as the nasopharynx or oropharynx, tonsils, about disease invasion and metastasis. Therefore, imaging
mediastinum, gastrointestinal tract, breast, pancreas, examinations play a critical role in treatment decisions
liver, spleen, mesentery, skin, and palate . The common and clinical management of patients with malignancy.
[1]
metastatic sites of FDCS are the liver, lung, lymph nodes, However, the correct diagnosis of this uncommon tumor
and peritoneum . In general, lung involvement typically was mainly based on histological examination at present,
[5]
represents metastatic disease . Primary pulmonary whether the Patlak analysis can distinguish lung cancer
[1]
FDCS, first described in 2001 by Shah et al., was an even from FDCS needs further study of large sample cases.
rarer occurrence, with only a few cases reported in the New and more specific non-invasive examinations
literature so far [6-12] . need to be developed for early detection of the disease.
There is no standard treatment regimen for FDCS up Moreover, considering the heterogeneity of FDCS, it is
to now. In reported primary pulmonary FDCS cases, most crucial to identify the biological or imaging features that
cases with the local disease received surgical excision can reflect or predict the high risk of tumor recurrence
of the tumor with or without post-operative adjuvant and metastasis. A corresponding post-operative
therapy such as chemotherapy and radiotherapy [6-12] . The examination is also necessary to determine if any lesions
patient of this case underwent surgical excision without remain.
any adjuvant therapy. Although some patients remained
disease free after surgery [7-9,12] , post-operative local 4. Conclusion
recurrence and/or distant metastasis occurred in certain We share our experience in hopes that corresponding
patients after initial treatment [6,8] . For our reported case, imaging and histopathological features will enhance
Volume 1 Issue 2 (2023) 4 https://doi.org/10.36922/arnm.0824