Page 36 - ARNM-2-1
P. 36
Advances in Radiotherapy
& Nuclear Medicine 99m Tc-DOX in multidrug resistance studies
A B C D
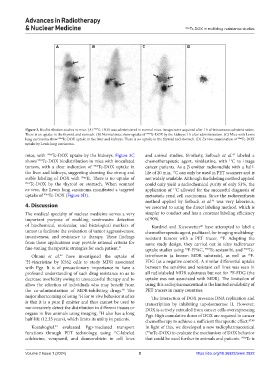
Figure 3. Biodistribution studies in mice. (A) Tc-DOX was administered in normal mice. Images were acquired after 1 h of intravenous administration.
99m
There is an uptake in the thyroid and stomach. (B) Normal mice show uptake of Tc-DOX by the kidneys 1 h after administration. (C) Mice with Lewis
99m
lung carcinoma show 99m Tc-DOX uptake in the liver and kidneys. There is no uptake in the thyroid and stomach. (D) Ex vivo examination of 99m Tc-DOX
uptake by Lewis lung carcinoma.
45
mice, with 99m Tc-DOX uptake by the kidneys. Figure 3C and animal studies. Similarly, Solbach et al. labeled a
shows 99m Tc-DOX biodistribution in mice with inoculated chemotherapeutic agent, vinblastine, with C to image
11
tumors, with a clear indication of 99m Tc-DOX uptake in cancer patients. As a β emitter radionuclide with a half-
the liver and kidneys, suggesting showing the strong and life of 20 min, C can only be used in PET scanners and is
11
stable labeling of DOX with 99m Tc. There is no uptake of not widely available. Although the labeling method applied
99m Tc-DOX by the thyroid or stomach. When scanned could only yield a radiochemical purity of only 53%, the
ex vivo, the Lewis lung carcinoma manifested a targeted application of C allowed for the successful diagnosis of
11
uptake of Tc-DOX (Figure 3D). metastatic renal cell carcinomas. Since the radiosynthesis
99m
method applied by Solbach et al. was very laborious,
45
4. Discussion we resorted to using the direct labeling method, which is
The medical specialty of nuclear medicine serves a very simpler to conduct and has a constant labeling efficiency
important purpose of enabling noninvasive detection of 90%.
of biochemical, molecular, and histological markers of Kurdziel and Kiesewetter have attempted to label a
46
tumor to facilitate the evaluation of tumor aggressiveness, chemotherapeutic agent, paclitaxel, for imaging multidrug-
invasiveness, and resistance to therapy. These findings resistant tumors with a PET tracer, F. Adopting the
18
from these applications may provide rational criteria for same study design, they carried out in vitro radiotracer
fine-tuning therapeutic strategies for each patient. 41 uptake studies using F-FPAC, 99m Tc-sestamibi, and 99m Tc-
18
18
Ohtani et al. have investigated the uptake of tetrofosmin (a known MDR substrate), as well as F-
42
3 H-vincristine by K562 cells to study MDR associated FDG (as a negative control). A similar differential uptake
with Pgp. It is of precautionary importance to have a between the sensitive and resistant cell lines was seen in
profound understanding of such drug resistance so as to all radiolabeled MDR substrates but not for F-FDG (the
18
decrease morbidity owing to unsuccessful therapy and to uptake was not associated with MDR). The limitation of
allow the selection of individuals who may benefit from using this radiopharmaceutical is the limited availability of
the co-administration of MDR-inhibiting drugs. The PET tracers in many countries.
43
major shortcoming of using H for in vivo behavior studies The interaction of DOX prevents DNA replication and
3
is that it is a pure β emitter and thus cannot be used to transcription by inhibiting topoisomerase II. However,
noninvasively detect the distribution in different tissues or DOX is actively extruded from cancer cells overexpressing
organs in live animals using imaging. H also has a long Pgp. High cumulative doses of DOX are required in cancer
3
half-life (12.33 years), which limits its utility in patients. chemotherapy to achieve a sufficient therapeutic effect. 47,48
44
Kostakoglul. evaluated Pgp-mediated transport In light of this, we developed a new radiopharmaceutical
99
functions through PET technology, using C-labeled ( mTc-DOX) to evaluate the mechanism of DOX behavior
11
colchicine, verapamil, and daunorubicin in cell lines that could be used further in animals and patients. 99m Tc is
Volume 2 Issue 1 (2024) 5 https://doi.org/10.36922/arnm.2822