Page 15 - ARNM-2-4
P. 15
Advances in Radiotherapy
& Nuclear Medicine Radionuclide-carrying liposomes
tumor microenvironments as opposed to extravasation into
healthy areas. Stolarz et al. developed a type of liposome
38
39
that offers control of release through X-ray irradiation. The
experiment utilized the fact that chloral hydrate releases
free protons after exposure to X-rays by incorporating it
into the liposomal structure. The study showed that the
treatment of tumors with liposomes paired with radiation
showed more intense therapeutic effects compared to
either the liposomes or radiation alone.
Prabhakar et al. reported that the performance of
40
liposomal drug delivery can be enhanced by directing
ultrasonic waves toward a tumor during treatment with
intravenously administered liposomes. Specifically, the
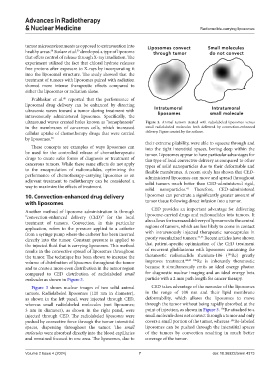
ultrasound waves created holes known as “sonophoresis” Figure 3. Animal tumors treated with radiolabeled liposomes versus
in the membranes of cancerous cells, which increased small radiolabeled molecules both delivered by convection-enhanced
cellular uptake of chemotherapy drugs that were carried delivery. Figure created by the authors.
by liposomes. 40
their extreme pliability, were able to squeeze through and
These concepts are examples of ways liposomes can into the tight interstitial spaces, boring deep within the
be used for the controlled release of chemotherapeutic tumor. Liposomes appear to have particular advantages for
drugs to create safer forms of diagnosis or treatment of this type of local convective delivery as compared to other
cancerous tumors. While these same effects do not apply types of solid nanoparticles due to their deformable and
to the encapsulation of radionuclides, optimizing the flexible membranes. A recent study has shown that CED-
performance of chemotherapy-carrying liposomes as an administered liposomes can move and spread throughout
adjuvant treatment to radiotherapy can be considered a solid tumors much better than CED-administered rigid,
way to maximize the effects of treatment.
solid nanoparticles. Therefore, CED-administered
41
10. Convection-enhanced drug delivery liposomes can penetrate a significantly greater amount of
with liposomes tumor tissue following direct infusion into a tumor.
CED provides an important advantage for delivering
Another method of liposome administration is through
“convection-enhanced delivery (CED)” for the local liposome-carried drugs and radionuclides into tumors. It
treatment of tumors. Convection, in this particular also allows for increased delivery of liposomes to the central
application, refers to the pressure applied to a catheter regions of tumors, which are less likely to come in contact
from a syringe pump where the catheter has been inserted with intravenously injected therapeutic nanocapsules in
directly into the tumor. Constant pressure is applied to poorly vascularized tumors. 42,43 Recent articles have shown
the injected fluid that is carrying liposomes. This method that patient-specific optimization of the CED treatment
results in the convective spread of liposomes throughout of recurrent glioblastoma with liposomes containing the
186
the tumor. The technique has been shown to increase the theranostic radionuclide rhenium-186 ( Re) greatly
volume of distribution of liposomes throughout the tumor improves treatment. 44,45 186 Re is inherently theranostic
and to create a more even distribution in the tumor region because it simultaneously emits an ideal energy photon
compared to CED distribution of radiolabeled small for diagnostic nuclear imaging and an ideal energy beta
molecules as shown in Figure 3. particle with a 2 mm path length for cancer therapy.
Figure 3 shows nuclear images of two solid animal CED takes advantage of the nanosize of the liposomes
tumors. Radiolabeled liposomes (120 nm in diameter), in the range of 100 nm and their lipid membrane
as shown in the left panel, were injected through CED, deformability, which allows the liposomes to move
whereas small radiolabeled molecules (not liposomes; through the tumor without being rapidly absorbed at the
186
3 nm in diameter), as shown in the right panel, were point of injection, as shown in Figure 3. Re attached to a
injected through CED. The radiolabeled liposomes were small molecule does not convect through a tumor and only
186
pushed by convective force through the tumor interstitial covers a small portion of the tumor, whereas Re-labeled
spaces, dispersing throughout the tumor. The small liposomes can be pushed through the interstitial spaces
molecules were absorbed directly into the blood capillaries of the tumors by convection resulting in much better
and remained focused in one area. The liposomes, due to coverage of the tumor.
Volume 2 Issue 4 (2024) 7 doi: 10.36922/arnm.4373