Page 32 - ARNM-3-1
P. 32
Advances in Radiotherapy
& Nuclear Medicine Chinese Expert Consensus for LACC
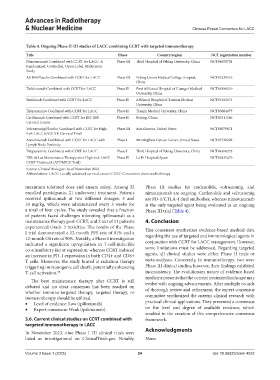
Table 4. Ongoing Phase II‑III studies of LACC combining CCRT with targeted immunotherapy
Title Phase Country/region NCT registration number
Nimotuzumab Combined with CCRT for LACC: A Phase III Third Hospital of Peking University, China NCT04678791
Randomized, Controlled, Open-Label, Multicenter
Study
AK104/Placebo Combined with CCRT for LACC Phase III Peking Union Medical College Hospital, NCT05235516
China
Tislelizumab Combined with CCRT for LACC Phase II First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi Medical NCT05588219
University, China
Sintilimab Combined with CCRT for LACC Phase II Affiliated Hospital of Xuzhou Medical NCT05105672
University, China
Tirapazamine Combined with CCRT for LACC Phase II Tianjin Medical University, China NCT05084677
Carilizumab Combined with CCRT for IB2-IIIB Phase II Beijing, China NCT05311566
Cervical Cancer
Volrustomig/Placebo Combined with CCRT for High- Phase III AstraZeneca, United States NCT06079671
Risk LACC (eVOLVE-Cervical Trial)
Atezolizumab Combined with CCRT for LACC with Phase I Birmingham Cancer Center, United States NCT03738228
Lymph Node Positivity
Tirapazamine Combined with CCRT for LACC Phase I Third Hospital of Peking University, China NCT04368273
TSR-042 as Maintenance Therapy after High-risk LACC Phase II La Fe Hospital, Spain NCT03833479
CCRT Treatment (ATOMICC Trial)
Source: ClinicalTrials.gov; As of November 2023.
Abbreviations: LACC: Locally advanced cervical cancer; CCRT: Concurrent chemoradiotherapy.
maximum tolerated dose and ensure safety. Among 32 Phase III studies for cardenolide, volrustomig, and
enrolled participants, 21 underwent treatment. Patients nimotuzumab are ongoing. Cardenolide and volrustomig
received ipilimumab at two different dosages: 3 and are PD-1/CTLA-4 dual antibodies, whereas nimotuzumab
10 mg/kg, which were administered every 3 weeks for is the only targeted agent being evaluated in an ongoing
a total of four cycles. The study revealed that a fraction Phase III trial (Table 4).
of patients faced challenges tolerating ipilimumab as a
maintenance therapy post-CCRT, and 2 out of 21 patients 4. Conclusion
experienced Grade 3 toxicities. The results of the Phase This consensus synthesizes evidence-based medical data
I trial demonstrated a 12-month PFS rate of 81% and a
12-month OS rate of 90%. Notably, a Phase I investigation regarding the use of targeted and immunological agents in
indicated a significant upregulation in T-cell-inducible conjunction with CCRT for LACC management. However,
co-stimulatory factor expression, whereas CCRT induced some limitations must be addressed. Regarding targeted
an increase in PD-1 expression in both CD4+ and CD8+ agents, all clinical studies were either Phase II trials or
T cells. Moreover, the study hinted at radiation therapy meta-analyses. Conversely, in immunotherapy, two were
triggering immunogenic cell death, potentially enhancing Phase III clinical studies; however, their findings exhibited
T-cell activation. 33 inconsistency. The evolutionary nature of evidence-based
medicine presents that the current treatment landscape may
The best maintenance therapy after CCRT is still
debated and no clear consensus has been reached on evolve with ongoing advancements. After multiple rounds
whether immune-targeted therapy, targeted therapy, or of thorough review and refinement, the expert consensus
immunotherapy should be utilized. committee synthesized the current clinical research with
• Level of evidence: Low (ipilimumab) practical clinical applications. They presented a consensus
• Expert consensus: Weak (ipilimumab). on the level and degree of available evidence, which
resulted in the creation of this comprehensive consensus
3.6. Current clinical studies on CCRT combined with framework.
targeted immunotherapy in LACC
Acknowledgments
In November 2023, nine Phase I–III clinical trials were
listed as investigational on ClinicalTrials.gov. Notably, None.
Volume 3 Issue 1 (2025) 24 doi: 10.36922/arnm.4032