Page 46 - ARNM-3-1
P. 46
Advances in Radiotherapy
& Nuclear Medicine EZH2 inhibition in ARID1A-deficient TNBC
stromal infiltration by proliferative CD8 T cells, FoxP3 durable anti-tumor response, ultimately leading to T-cell
+
+
Tregs, and immune cells expressing checkpoint regulators exhaustion and checkpoint activation, suggesting that
PD-1 and LAG-3. Following 4 weeks of tazemetostat altering the epigenetic landscape may sensitize some
110
treatment and subsequent radiotherapy to the primary tumors to checkpoint inhibitors. 110
tumor site, a complete response was observed at distant
metastatic sites. However, at the primary treatment Radiotherapy can induce immunogenic cell death,
110
site, which received a dose of 70 Gy in 35 fractions, only characterized by the release of danger-associated molecular
a partial response was noted. The authors speculated that pattern antigens that trigger the uptake of antigens and
radiotherapy at the sacrum likely depleted the TILs induced activation of APCs, leading to the priming of cytotoxic
by tazemetostat, rendering the sacral mass less responsive lymphocytes and an adaptive immune response. However,
110
to immunotherapy. The patient was subsequently treated the precise contribution of EZH2 inhibition, radiotherapy,
110
with ICIs. This strategy of EZH2 inhibition fostered a and PD-1/PD-L1 blockade on the immunologic and overall
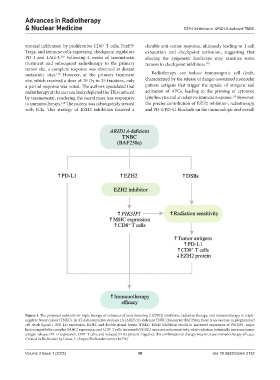
Figure 4. The proposed rationale for triple therapy of enhancer of zeste homolog 2 (EZH2) inhibition, radiation therapy, and immunotherapy in triple-
negative breast cancer (TNBC). In AT-rich interactive domain 1A (ARID1A)-deficient TNBC (biomarker BAF250a), there is an increase in programmed
cell death ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression, EZH2, and double-strand breaks (DSBs). EZH2 inhibition results in increased expression of PIK3IP1, major
histocompatibility complex (MHC) expression, and CD8 T cells. Increased PIK3IP1 increases radiosensitivity, while radiation potentially increases tumor
+
antigen release, PD-L1 expression, CD8 T cells, and reduced EZH2 protein. Together, this combinational therapy may increase immunotherapy efficacy.
+
Created in BioRender by Lukas, L. (https://BioRender.com/e14a778).
Volume 3 Issue 1 (2025) 38 doi: 10.36922/arnm.5132