Page 103 - ARNM-3-2
P. 103
Advances in Radiotherapy
& Nuclear Medicine A dosimetric research on iodine-125 seed implantation
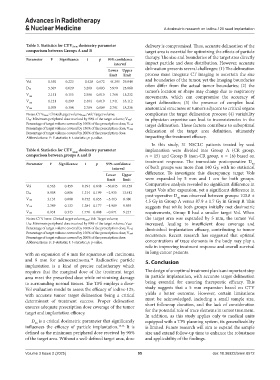
Table 3. Statistics for CTV 5mm dosimetry parameter delivery is compromised. Thus, accurate delineation of the
comparison between Groups A and B target area is essential for optimizing the effects of particle
Parameter F Significance t p 95% confidence therapy. The size and boundaries of the target area directly
interval impact particle and dose distribution. However, accurate
Lower Upper delineation presents several challenges: (1) The delineation
limit limit process must integrate CT imaging to ascertain the size
Vol 1.550 0.223 −0.428 0.672 −44.395 29.048 and boundaries of the tumor, yet the imaging boundaries
often differ from the actual tumor boundaries; (2) the
D90 5.307 0.029 3.280 0.003 5.979 25.868 tumor’s location or shape may change due to respiratory
V 2.131 0.155 2.586 0.015 1.768 15.232
100 movements, which can compromise the accuracy of
V 1.121 0.299 2.484 0.019 1.741 18.112
150 target delineation; (3) the presence of complex local
V200 1.078 0.308 2.789 0.009 2.791 18.236 anatomical structures or tumors adjacent to critical organs
Notes: CTV5mm: Clinical target volume5mm; Vol: Target volume; complicates the target delineation process; (4) variability
D90: Minimum peripheral dose received by 90% of the target volume; V100: in physician expertise can lead to inconsistencies in the
Percentage of target volume covered by 100% of the prescription dose; V150: target delineation. These factors contribute to suboptimal
Percentage of target volume covered by 150% of the prescription dose; V200: delineation of the target area definition, ultimately
Percentage of target volume covered by 200% of the prescription dose.
Abbreviations: F: F-statistic; t: t-statistic; p: p-value. impacting the treatment efficacy.
In this study, 31 NSCLC patients treated by seed
Table 4. Statistics for CTV 1mm dosimetry parameter implantation were divided into Group A (CR group,
comparison between groups A and B n = 15) and Group B (non-CR group, n = 16) based on
treatment response. The immediate post-operative D
Parameter F Significance t p 95% confidence 90
interval of both groups was more than 140 Gy, with no statistical
Lower Upper difference. To investigate this discrepancy, target Vols
limit limit were expanded by 5 mm and 1 cm for both groups.
Vol 0.563 0.459 0.194 0.848 −50.845 61.458 Comparative analysis revealed no significant difference in
target Vols after expansion, yet a significant difference in
D90 8.958 0.006 1.314 0.199 −2.935 13.442 post-operative D was observed between groups: 103.8 ±
90
V100 3.134 0.088 0.452 0.655 −5.413 8.480 4.5 Gy in Group A versus 87.9 ± 1.7 Gy in Group B. This
2.389 0.133 1.384 0.177 −1.909 9.855
V150 suggests that while both groups initially met dosimetric
V200 0.931 0.343 1.770 0.088 −0.671 9.217 requirements, Group B had a smaller target Vol. When
Notes: CTV1mm: Clinical target volume1mm; Vol: Target volume; the target area was expanded by 5 mm, the tumor Vol
D90: Minimum peripheral dose received by 90% of the target volume; V100: increased, leading to insufficient dose coverage and
Percentage of target volume covered by 100% of the prescription dose; V150: diminished implantation efficacy, contributing to tumor
Percentage of target volume covered by 150% of the prescription dose; V200: recurrence. Recent research has suggested that optimal
Percentage of target volume covered by 200% of the prescription dose.
Abbreviations: F: F-statistic; t: t-statistic; p: p-value. concentrations of trace elements in the body may play a
role in improving treatment response and overall survival
with an expansion of 6 mm for squamous cell carcinoma in lung cancer patients.
and 8 mm for adenocarcinoma. Radioactive particle 5. Conclusion
14
implantation is a kind of precise radiotherapy which
requires that the marginal dose of the treatment target The design of an optimal treatment plan is an important step
area meet the prescribed dose while minimizing damage in particle implantation, with accurate target delineation
to surrounding normal tissues. The TPS employs a dose- being essential for ensuring therapeutic efficacy. This
Vol evaluation model to assess the efficacy of iodine-125, study suggests that a 5 mm expansion based on CTV
with accurate tumor target delineation being a critical yields a better outcome. However, certain limitations
determinant of treatment success. Proper delineation must be acknowledged, including a small sample size,
ensures adequate prescription dose coverage of the tumor short follow-up duration, and the lack of consideration
target and implantation efficacy. for the potential role of trace elements in tumor treatment.
In addition, as this study applies only to medical units
D is a critical dosimetric parameter that significantly equipped with a TPS planning system, its generalizability
90
influences the efficacy of particle implantation. 15,16 It is is limited. Future research will aim to expand the sample
defined as the minimum peripheral dose received by 90% size and extend follow-up time to enhance the robustness
of the target area. Without a well-defined target area, dose and applicability of the findings.
Volume 3 Issue 2 (2025) 95 doi: 10.36922/arnm.8512