Page 9 - BH-1-2
P. 9
Brain & Heart Post-stroke atrial fibrillation and predictive scores
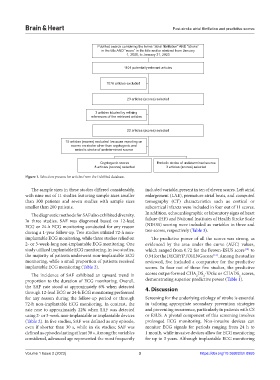
PubMed search combining the terms “atrial fibrillation” AND “stroke”
in the title AND “score” in the title and/or abstract from January
1, 2000, to January 31, 2023
1101 potentially relevant articles
1078 articles excluded
23 articles (scores) selected
3 articles icluded by refining
references of the retrieved articles
23 articles (scores) selected
15 articles (scores) excluded because reporting on
scores on stroke other than cryptogenic and
embolic stroke of undetermined source
Cryptogenic scores Embolic stroke of undetermined source
8 articles (scores) selected 3 articles (scores) selected
Figure 1. Selection process for articles from the PubMed database.
The sample sizes in these studies differed considerably, included variable, present in ten of eleven scores. Left atrial
with nine out of 11 studies featuring sample sizes smaller enlargement (LAE), premature atrial beats, and computed
than 300 patients and seven studies with sample sizes tomography (CT) characteristics such as cortical or
smaller than 200 patients. subcortical infarcts were included in four out of 11 scores.
The diagnostic methods for SAF also exhibited diversity. In addition, echocardiographic or laboratory signs of heart
In three studies, SAF was diagnosed based on 12-lead failure (HF) and National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale
ECG or 24-h ECG monitoring conducted for any reason (NIHSS) scoring were included as variables in three and
during a 1-year follow-up. Two studies utilized 72-h non- two scores, respectively (Table 3).
implantable ECG monitoring, while three studies relied on The predictive power of all the scores was strong, as
2- or 3-week-long non-implantable ECG monitoring. One evidenced by the area under the curve (AUC) values,
study utilized implantable ECG monitoring. In two studies, which ranged from 0.72 for the Brown-ESUS score to
[15]
the majority of patients underwent non-implantable ECG 0.94 for the DECRYPTORING score . Among the studies
[13]
monitoring, while a small proportion of patients received reviewed, five included a comparator for the predictive
implantable ECG monitoring (Table 2). scores. In four out of these five studies, the predictive
The incidence of SAF exhibited an upward trend in scores outperformed CHA DS -VASc or CHADS scores,
2
2
2
proportion to the duration of ECG monitoring. Overall, demonstrating superior predictive power (Table 1).
the SAF rate stood at approximately 6% when detected 4. Discussion
through 12-lead ECG or 24-h ECG monitoring performed
for any reason during the follow-up period or through Screening for the underlying etiology of stroke is essential
72-h non-implantable ECG monitoring. In contrast, the in tailoring appropriate secondary prevention strategies
rate rose to approximately 22% when SAF was detected and preventing recurrence, particularly in patients with CS
using 2- or 3-week non-implantable or implantable devices or ESUS. A pivotal component of this screening involves
(Table 2). In five studies, SAF was defined as any episode, prolonged ECG monitoring. Non-invasive devices can
even if shorter than 30 s, while in six studies; SAF was monitor ECG signals for periods ranging from 24 h to
defined as episodes lasting at least 30 s. Among the variables 1 month, while invasive devices allow for ECG monitoring
considered, advanced age represented the most frequently for up to 3 years. Although implantable ECG monitoring
Volume 1 Issue 2 (2023) 3 https://doi.org/10.36922/bh.0955