Page 89 - BH-2-1
P. 89
Brain & Heart QTc interval in BMS
taking medications that affect the QTc interval, and with unexplained pain such as BMS, fibromyalgia, back
(iii) patients with comorbid psychiatric disorders or taking pain, and headache have an enhanced salience network
psychotropic medications. The degree of pain was examined activity, decreased functional connectivity between the
using a visual analog scale (VAS), with 0 representing no default mode network and the executive control network,
pain and 100 representing the worst pain ever. The pain and decreased functional connectivity between the default
catastrophizing scale (PCS) was used to assess negative mode network and the descending pain inhibitory pathway.
5
feelings associated with pain. The QTc interval according The salience network is strongly functionally coupled
4
to Bazett’s formula was used as a measure of autonomic to the dopaminergic reward system of the basal ganglia
tone. Correlations between variables were examined and increases sympathetic tone in the hypothalamus. In
using Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient. All patients our study, PCS was negatively correlated with the QTc
provided written informed consent for participating in interval, indicating that patients with destructive feelings
this study. The personally identifiable information was not of pain had a shortened QTc interval. Recent studies have
disclosed throughout the study to ensure anonymity and shown that the QTc interval is associated with autonomic
privacy. We were able to accumulate data from a total of imbalance and tends to shorten with sympathetic tone.
6
51 BMS patients: 11 males (21.5%) and 40 females (78.5%) The QTc interval reflects the degree of sympathetic tone
with a mean age of 61.2 ± 1.6 years (mean ± SE). The VAS, under certain conditions, such as the absence of cardiac
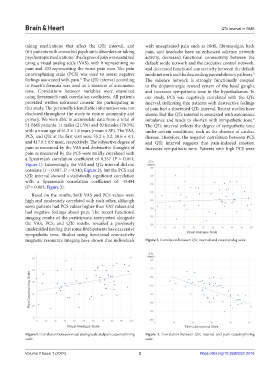
PCS, and QTc at the first visit were 55.2 ± 3.2, 30.6 ± 4.1, disease. Therefore, the negative correlation between PCS
and 417.8 ± 6.9 msec, respectively. The subjective degree of and QTc interval suggests that pain-induced emotion
pain as measured by the VAS and destructive thoughts of increases sympathetic tone. Patients with high PCS were
pain as measured by the PCS were mildly correlated with
a Spearman’s correlation coefficient of 0.357 (P = 0.011;
Figure 1). Interestingly, the VAS and QTc interval did not
correlate (r = 0.087, P = 0.540; Figure 2), but the PCS and
QTc interval showed a statistically significant correlation
with a Spearman’s correlation coefficient of −0.404
(P = 0.003; Figure 3).
Based on the results, both VAS and PCS values were
high and moderately correlated with each other, although
some patients had PCS values higher than VAS values and
had negative feelings about pain. The recent functional
imaging results of the participants, interpreted alongside
the VAS, PCS, and QTc results, revealed a previously
unidentified finding that some BMS patients have excessive
sympathetic tone. Studies using functional connectivity
magnetic resonance imaging have shown that individuals Figure 2. Correlation between QTc interval and visual analog scale.
Figure 1. Correlation between visual analog scale and pain catastrophizing Figure 3. Correlation between QTc interval and pain catastrophizing
scale. scale.
Volume 2 Issue 1 (2024) 2 https://doi.org/10.36922/bh.2016