Page 31 - BH-2-3
P. 31
Brain & Heart Digital tools for stroke and bleeding risk in AF (Cont’d...)
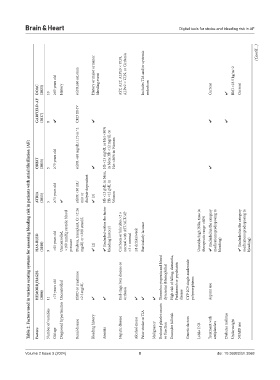
DOAC (2023) 10 ≥65 years old History eGFR≤60 mL/min History or major or minor bleeding event AST, ALT, ALP≥3 × ULN, ALP≥2 × ULN, or Cirrhosis Includes TIA and/or systemic embolism Current ✔ BMI <18.5 kg/m^2 Current
GARFIELD‑AF (2017) 8 ✔ CKD III-IV ✔ ✔ ✔
eGFR <60 mg/dL/1.73 m^2 Hb <13 mg/dL or Hct <40% in Men; Hb <12 mg/dL or Hct <36% in Women
Table 2. Factors used in various scoring systems for assessing bleeding risk in patients with atrial fibrillation (AF)
ORBIT (2015) 5 ≥75 years old ✔ ✔
ATRIA (2011) 5 ≥75 years old ✔ eGFR <30 mL/ min or dialysis-dependent ✔ (3) Hb <13 g/dL in Men; Hb <12 g/dL in Women
>160 mmHg systolic blood Dialysis, transplant, Cr >2.26 mg/dL or >200 µmol/L ✔ (Included within the factor Cirrhosis or bilirubin >2 × normal with AST/ALT/AP Unstable/high INRs, time in therapeutic range <60% ✔ (Included in the category medications predisposing to ✔ (Included in the category medications predisposing to
HAS‑BLED (2010) 9 >65 years old Uncontrolled, pressure ✔ (2) bleeding history) >3 × normal ≥8 drinks/week Particularly lacunar bleeding) bleeding)
HEMORR 2 HAGES (2006) 11 >75 years old Uncontrolled ESRD or creatinine >2.5 mg/dL ✔ ✔ End-stage liver disease or cirrhosis ✔ ✔ ✔ Thrombocytopenia and blood dyscrasias (Hemophilia) High risk of falling, dementia, Parkinson’s or psychiatric disease CYP 2C9 single-nucleotide polymorphisms Aspirin use
Number of variables Diagnosed hypertension Bleeding history Hepatic disease Prior stroke or TIA Reduced platelet counts Excessive fall risk Genetic factors Treatment with Diabetes mellitus
Factors Old age Renal disease Anemia Alcohol excess Malignancy or function Labile INR antiplatelets Underweight NSAID use
Volume 2 Issue 3 (2024) 8 doi: 10.36922/bh.3068