Page 76 - BH-2-3
P. 76
Brain & Heart Lipids in ALS: Bad and beneficial
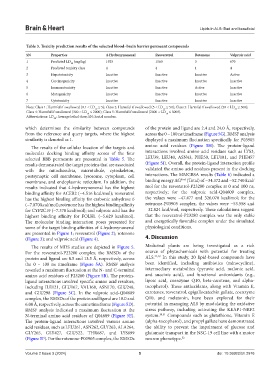
Table 3. Toxicity prediction results of the selected blood–brain barrier permeant compounds
SN Properties 4‑Hydroxynonenal Resveratrol Rotenone Valproic acid
1 Predicted LD (mg/kg) 1925 1560 3 670
50
2 Predicted toxicity class 4 4 1 4
3 Hepatotoxicity Inactive Inactive Inactive Active
4 Carcinogenicity Inactive Inactive Inactive Inactive
5 Immunotoxicity Inactive Inactive Active Inactive
6 Mutagenicity Inactive Inactive Inactive Inactive
7 Cytotoxicity Inactive Inactive Inactive Inactive
Note: Class 1: Harmful if swallowed (0.1 < LD ≤ 5); Class 2: Harmful if swallowed (5 < LD ≤ 50); Class 3: Harmful if swallowed (50 < LD ≤ 300);
50
50
50
Class 4: Harmful if swallowed (300 < LD ≤ 2000); Class 5: Harmful if swallowed (2000 < LD ≤ 5000).
50
50
Abbreviations: LD : Average lethal dose; SN: Serial number.
50
which determines the similarity between compounds of the protein and ligand are 2.4 and 24.0 Å, respectively,
from the reference and query targets, where the highest across the 0 – 100 ns timeframe (Figure 5G). RMSF analysis
similarity is denoted as 1. displayed a maximum fluctuation specifically for P03905
The results of the cellular location of the targets and amino acid residues (Figure 5H). The protein-ligand
molecular docking binding affinity scores of the four interactions involved amino acid residues such as LYS3,
selected BBB permeants are presented in Table 5. The LEU39, LEU40, ASN43, PHE50, LEU181, and PHE457
results demonstrated the target proteins that are associated (Figure 5I). Overall, the protein-ligand interaction profile
with the mitochondria, microtubule, cytoskeleton, validated the amino acid residues present in the docking
postsynaptic cell membrane, lysosome, cytoplasm, cell interactions. The MMGBSA results (Table 6) indicated a
membrane, and endoplasmic reticulum. In addition, the binding energy ΔG bind (Total) of −34.372 and −52.740 kcal/
results indicated that 4-hydroxynonenal has the highest mol for the resveratrol-P23280 complex at 0 and 100 ns,
binding affinity for ACER2 (−4.516 kcal/mol); resveratrol respectively; for the valproic acid-Q04609 complex,
has the highest binding affinity for carbonic anhydrase 6 the values were −47.477 and 326.070 kcal/mol; for the
(−7.070 kcal/mol); rotenone has the highest binding affinity rotenone-P03905 complex, the values were −53.558 and
for CYP2C19 (−7.378 kcal/mol); and valproic acid has the −32.824 kcal/mol, respectively. These calculations suggest
highest binding affinity for FOLH1 (−5.629 kcal/mol). that the resveratrol-P23280 complex was the only stable
The molecular binding interaction poses presented for and energetically favorable complex under the simulated
some of the target binding affinities of 4-hydroxynonenal physiological conditions.
are presented in Figure 1; resveratrol (Figure 2); rotenone
(Figure 3); and valproic acid (Figure 4). 4. Discussion
The results of MDS studies are depicted in Figure 5. Medicinal plants are being investigated as a rich
For the resveratrol-P23280 complex, the RMSDs of the source of phytochemicals with potential for treating
protein and ligand are 8.5 and 13.5 Å, respectively, across ALS. 22,29 In this study, 20 lipid-based compounds have
the 0 – 100 ns timeframe (Figure 5A). RMSF analysis been identified, including antibiotics (minocycline),
revealed a maximum fluctuation at the N- and C-terminal intermediary metabolites (pyruvic acid, malonic acid,
amino acid residues of P23280 (Figure 5B). The protein- and succinic acid), and functional antioxidants (e.g.,
ligand interactions involved specific amino acid residues, lipoic acid, coenzyme Q10, beta-carotene, and alpha-
including ILE121, GLU167, VAL168, ASN170, GLU248, tocopherol). These antioxidants, along with Vitamin E,
and GLU298 (Figure 5C). In the valproic acid-Q04609 carotenes, resveratrol, epigallocatechin gallate, coenzyme
complex, the RMSDs of the protein and ligand are 10.0 and Q10, and melatonin, have been explored for their
6.00 Å, respectively, across the same timeframe (Figure 5D). potential in managing ALS by modulating the oxidative
RMSF analysis indicated a maximum fluctuation at the stress pathway, including activating the KEAP1-NRF2
N-terminal amino acid residues of Q04609 (Figure 5E). system. 30,31 Compounds such as glutathione, Vitamin E
The protein-ligand interactions involved various amino (alpha-tocopherol), and propyl gallate have demonstrated
acid residues, such as LEU261, ASN262, GLY263, ALA264, the ability to prevent the impairment of glucose and
GLY265, GLY427, GLU522, THR687, and LYS699 glutamate transport in the NSC-19 cell line with a motor
(Figure 5F). For the rotenone-P03905 complex, the RMSDs neuron phenotype. 32
Volume 2 Issue 3 (2024) 5 doi: 10.36922/bh.2976