Page 82 - BH-2-3
P. 82
Brain & Heart Lipids in ALS: Bad and beneficial
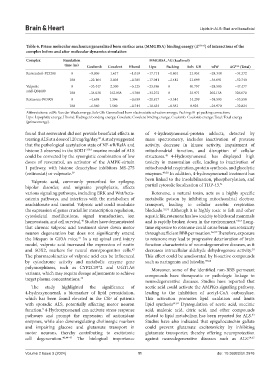
Table 6. Prime molecular mechanics/generalized born surface area (MMGBSA) binding energy (Δ Gbind ) of interactions of the
complex before and after molecular dynamics simulation
Complex Simulation MMGBSA, ΔG (kcal/mol)
time (ns) Coulomb Covalent Hbond Lipo Packing Solv_GB vdW ΔG bind (Total)
Resveratrol-P23280 0 −9.006 1.617 −1.019 −17.711 −1.861 21.954 −28.344 −34.372
100 −22.164 2.003 −0.705 −17.041 −2.442 21.699 −34.091 −52.740
Valproic 0 −33.447 2.300 −5.125 −23.496 0 40.797 −28.505 −47.477
acid-Q04609 100 −34.038 162.038 −4.788 −33.272 0 33.971 202.158 326.070
Rotenone-P03905 0 −4.659 1.396 −0.639 −21.817 −3.544 14.299 −38.593 −53.558
100 −6.560 1.560 −0.744 −10.654 −0.381 8.925 −24.970 −32.824
Abbreviations: vdW: Van der Waals energy; Solv GB: Generalized born electrostatic solvation energy; Packing: Pi-pi packing correction;
Lipo: Lipophilic energy; Hbond: Hydrogen bonding energy; Covalent: Covalent binding energy; Coulomb: Coulomb energy; Total: Total energy
(prime energy).
found that resveratrol did not provide beneficial effects in of 4-hydroxynonenal-protein adducts, detected by
treating ALS at a dose of 120 mg/kg/day. A study suggested mass spectrometry, includes inactivation of protease
38
that the pathological acetylation state of NF-κB/RelA and activity, decrease in kinase activity, impairment of
histone 3 observed in the SOD1 G93A murine model of ALS mitochondrial function, and disruption of cellular
could be corrected by the synergistic combination of low structures. 48 4-Hydroxynonenal has displayed high
doses of resveratrol, an activator of the AMPK-sirtuin toxicity in mammalian cells, leading to inactivation of
1 pathway, with histone deacetylase inhibitors MS-275 mitochondrial respiration, protein synthesis, and glycolytic
(entinostat) or valproate. 39 enzymes. 49,50 In addition, 4-hydroxynonenal treatment has
Valproic acid, commonly prescribed for epilepsy, been linked to the insolubilization, phosphorylation, and
bipolar disorder, and migraine prophylaxis, affects partial cytosolic localization of TDP-43. 51
various signaling pathways, including ERK and Wnt/beta- Rotenone, a natural toxin, acts as a highly specific
catenin pathways, and interferes with the metabolism of metabolic poison by inhibiting mitochondrial electron
arachidonate and inositol. Valproic acid could modulate transport, leading to cellular aerobic respiration
the expression of genes crucial for transcription regulation, blockade. 52,53 Although it is highly toxic to fish and other
cytoskeletal modifications, signal transduction, ion aquatic life, rotenone has low toxicity to birds and mammals
homeostasis, and cell survival. Studies have demonstrated and is rapidly broken down in the environment. 54,55 Long-
40
that chronic valproic acid treatment slows down motor time exposure to rotenone could cause brain neurotoxicity
neuron degeneration but does not significantly extend through sufficient BBB permeation. 56,57 Therefore, exposure
the lifespan in G93A mice. In a rat spinal cord injury to rotenone may lead to progressive deterioration of brain
41
model, valproic acid increased the expression of nestin function characteristic of neurodegenerative diseases, as it
and SOX2, markers for neural stem/progenitor cells. decreases intracellular aldehyde dehydrogenase activity.
58
42
The pharmacokinetics of valproic acid can be influenced This effect could be ameliorated by bioactive compounds
by cytochrome activity and metabolic enzyme gene such as naringenin and luteolin. 59,60
polymorphisms, such as CYP2C19*2 and UGT1A6 Moreover, some of the identified non-BBB permeant
variants, which may require dosage adjustments to achieve compounds have therapeutic or pathologic linkage to
target plasma concentrations. 43 neurodegenerative diseases. Studies have reported that
The study highlighted the significance of acetic acid could activate the AMPKα signaling pathway,
4-hydroxynonenal, a biomarker of lipid peroxidation, leading to the inhibition of acetyl-CoA carboxylase.
which has been found elevated in the CSF of patients This activation promotes lipid oxidation and limits
with sporadic ALS, potentially affecting motor neuron lipid synthesis 61,62 Dysregulation of acetic acid, succinic
function. 4-Hydroxynonenal can activate stress response acid, malonic acid, citric acid, and other compounds
9
pathways and prompt the expression of antioxidant related to lipid metabolism has been reported for ALS.
63
enzymes, while also downregulating cholinergic markers Studies have also indicated that epigallocatechin gallate
and impairing glucose and glutamate transport in could prevent glutamate excitotoxicity by inhibiting
motor neurons, thereby contributing to excitotoxic glutamate transporter, thereby offering neuroprotection
cell degeneration. 40,44-47 The biological importance against neurodegenerative diseases such as ALS. 64,65
Volume 2 Issue 3 (2024) 11 doi: 10.36922/bh.2976