Page 11 - BH-3-3
P. 11
Brain & Heart Advances in stroke treatment
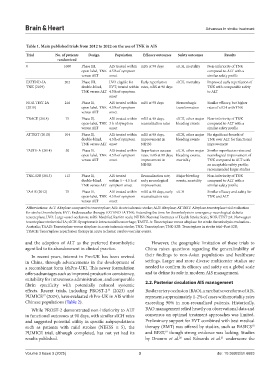
Table 1. Main published trials from 2012 to 2022 on the use of TNK in AIS
Trial No. of patients Design Population Efficacy outcomes Safety outcomes Results
randomized
0 1600 Phase III, AIS treated within mRS at 90 days sICH, mortality Non-inferiority of TNK
open-label, TNK 4.5 h of symptom compared to ALT with a
versus ALT onset similar safety profile
EXTEND-IA 202 Phase III, LVO eligible for Early reperfusion sICH, mortality Improved early reperfusion of
TNK (2019) double-blind, EVT, treated within rates, mRS at 90 days TNK with comparable safety
TNK versus ALT 4.5 h of symptom to ALT
onset
NOR-TEST 2A 216 Phase II, AIS treated within mRS at 90 days Hemorrhagic Similar efficacy, but higher
(2019) open-label, TNK 4.5 h of symptom transformation rates of sICH with TNK
versus ALT onset
TRACE (2018) 75 Phase II, AIS treated within mRS at 90 days, sICH, other major Non-inferiority of TNK
open-label, TNK 3 h of symptom recanalization rates bleeding events compared to ALT with a
versus ALT onset similar safety profile
ATTEST (2015) 104 Phase II, AIS treated within mRS at 90 days, sICH, other major No significant benefit of
double-blind, 4.5 h of symptom improvement in bleeding events TNK over ALT for functional
TNK versus ALT onset NIHSS improvement
TASTE-A (2014) 50 Phase II, AIS treated within Reperfusion success sICH, other major Similar reperfusion rates and
open-label, TNK 4.5 h of symptom rates, mRS at 90 days, bleeding events, neurological improvement of
versus ALT onset improvement in mortality TNK compared to ALT with
NIHSS an acceptable safety profile;
recommended larger studies
TNK-S2B (2013) 112 Phase II, AIS treated Recanalization rate, Major bleeding Non-inferiority of TNK
double-blind, within 3 – 4.5 h of early neurological events, mortality compared to ALT with a
TNK versus ALT symptom onset improvement similar safety profile
TAAIS (2012) 75 Phase II, AIS treated within mRS at 90 days, early sICH Similar efficacy and safety for
open-label, TNK 4.5 h of symptom recanalization rate TNK and ALT
versus ALT onset
Abbreviations: AcT: Alteplase compared to tenecteplase; AIS: Acute ischemic stroke; ALT: Alteplase; ATTEST: Alteplase-tenecteplase trial evaluation
for stroke thrombolysis; EVT: Endovascular therapy; EXTEND-IA TNK: Extending the time for thrombolysis in emergency neurological deficits–
tenecteplase; LVO: Large vessel occlusion; mRS: Modified Rankin scale; NIHSS: National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale; NOR-TEST 2A: Norwegian
tenecteplase stroke trial 2A; sICH: Symptomatic intracranial hemorrhage; TASTE-A: Tenecteplase versus alteplase for stroke thrombolysis evaluation–
Australia; TAAIS: Tenecteplase versus alteplase in acute ischemic stroke; TNK: Tenecteplase; TNK-S2B: Tenecteplase in stroke trial–Part S2B;
TRACE: Tenecteplase reperfusion therapy in acute ischemic cerebrovascular events.
and the adoption of ALT as the preferred thrombolytic However, the geographic limitation of these trials to
agent led to its abandonment in clinical practice. China raises questions regarding the generalizability of
In recent years, interest in Pro-UK has been revived their findings to non-Asian populations and healthcare
in China, through advancements in the development of settings. Larger and more diverse multicenter studies are
a recombinant form (rhPro-UK). This newer formulation needed to confirm its efficacy and safety on a global scale
offers advantages such as improved production consistency, and to define its role in modern AIS management.
suitability for intravenous administration, and comparable
fibrin specificity with potentially reduced systemic 2.2. Posterior circulation AIS management
effects. Recent trials, including PROST-2 (2023) and Basilar artery occlusion (BAO), a rare but severe form of AIS,
16
PUMICE (2024), have evaluated rhPro-UK in AIS within represents approximately 1-2% of cases with mortality rates
17
Chinese populations (Table 2). exceeding 90% in non-recanalized patients. Historically,
While PROST-2 demonstrated non-inferiority to ALT BAO management relied heavily on observational data and
in functional outcomes at 90 days, with similar sICH rates consensus on optimal treatment approaches was limited.
and suggested potential utility in specific subpopulations Preliminary support for EVT combined with best medical
18
such as patients with mild strokes (NIHSS ≤ 5), the therapy (BMT) was offered by studies, such as BASICS
19
PUMICE trial, although completed, has not yet had its and BEST, though strong evidence was lacking. Studies
results published. by Drumm et al. and Edwards et al. underscore the
21
20
Volume 3 Issue 3 (2025) 3 doi: 10.36922/bh.6683