Page 13 - BH-3-3
P. 13
Brain & Heart Advances in stroke treatment
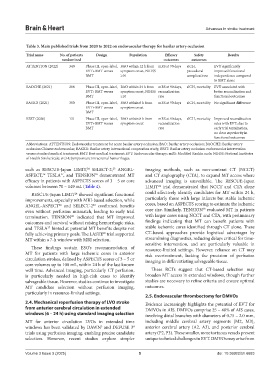
Table 3. Main published trials from 2020 to 2022 on endovascular therapy for basilar artery occlusion
Trial name No. of patients Design Population Efficacy Safety Results
randomized outcomes outcomes
ATTENTION (2022) 340 Phase III, open-label, BAO within 12 h from mRS at 90 days sICH, EVT significantly
EVT+BMT versus symptom onset, NIHSS procedural improved functional
BMT ≥10 complications independence compared
to BMT alone
BAOCHE (2021) 208 Phase III, open-label, BAO within 24 h from mRS at 90 days, sICH, mortality EVT associated with
EVT+BMT versus symptom onset, NIHSS recanalization better recanalization and
BMT ≥10 rate functional outcomes
BASICS (2021) 300 Phase III, open-label, BAO within 6 h from mRS at 90 days sICH, mortality No significant difference
EVT+BMT versus symptom onset
BMT
BEST (2020) 131 Phase III, open-label, BAO within 8 h from mRS at 90 days, sICH, mortality Improved recanalization
EVT+BMT versus symptom onset recanalization rates with EVT; due to
BMT rate early trial termination,
no clear superiority in
functional outcomes
Abbreviations: ATTENTION: Endovascular treatment for acute basilar artery occlusion; BAO: Basilar artery occlusion; BAOCHE: Basilar artery
occlusion Chinese endovascular; BASICS: Basilar artery international cooperation study; BEST: Basilar artery occlusion endovascular intervention
versus standard medical treatment; BMT: Best medical treatment; EVT: Endovascular therapy; mRS: Modified Rankin scale; NIHSS: National Institutes
of Health Stroke Scale; sICH: Symptomatic intracranial hemorrhages.
such as RESCUE-Japan LIMIT, SELECT-2, ANGEL- imaging methods, such as non-contrast CT (NCCT)
25
24
ASPECT, TESLA , and TENSION demonstrated MT and CT angiography (CTA), to expand MT access where
27
26
28
efficacy in patients with ASPECTS scores of 3 – 5 or core advanced imaging is unavailable. The RESCUE-Japan
volumes between 70 – 149 mL (Table 4). LIMIT trial demonstrated that NCCT and CTA alone
24
RESCUE-Japan LIMIT showed significant functional could effectively identify candidates for MT within 24 h,
24
improvements, especially with MRI-based selection, while particularly those with large infarcts but stable ischemic
26
25
ANGEL-ASPECT and SELECT-2 confirmed benefits cores, based on ASPECTS scoring to estimate the ischemic
28
even without perfusion mismatch, leading to early trial core size. Similarly, TENSION evaluated MT in patients
termination. TENSION indicated that MT improved with larger cores using NCCT and CTA, with preliminary
28
outcomes and survival without raising hemorrhagic risks, findings indicating that MT can benefit patients with
and TESLA hinted at potential MT benefits despite not stable ischemic cores identified through CT alone. These
27
fully achieving primary goals. The LASTE trial supported CT-based approaches provide logistical advantages by
29
MT within a 7-h window with MRI selection. streamlining diagnostics, reducing delays critical for time-
sensitive intervention, and are particularly valuable in
These findings sustain ESO’s recommendation of resource-limited settings. However, reliance on CT may
MT for patients with large ischemic cores in anterior risk overtreatment, lacking the precision of perfusion
circulation strokes, defined by ASPECTS scores of 3 – 5 or imaging in differentiating salvageable tissue.
core volumes up to 100 mL, within 24 h of the last known
well time. Advanced imaging, particularly CT perfusion, These RCTs suggest that CT-based selection may
is particularly needed in high-risk cases to identify broaden MT access in extended windows, though further
salvageable tissue. However, studies continue to investigate studies are necessary to refine criteria and ensure optimal
MT candidate selection without perfusion imaging, outcomes.
particularly in resource-limited settings.
2.5. Endovascular thrombectomy for DMVOs
2.4. Mechanical reperfusion therapy of LVO stroke Evidence increasingly highlights the potential of EVT for
from anterior cerebral circulation in extended DMVOs in AIS. DMVOs comprise 25 – 40% of AIS cases,
windows (6 – 24 h) using standard imaging selection involving distal branches with diameters of 0.75 – 2.0 mm,
MT for anterior circulation LVOs in extended time including middle cerebral artery segments (M2, M3),
windows has been validated by DAWN and DEFUSE 3 anterior cerebral artery (A2, A3), and posterior cerebral
4
5
trials using perfusion imaging, enabling precise candidate artery (P2, P3). These smaller, more tortuous vessels present
selection. However, recent studies explore simpler unique technical challenges in EVT. DMVOs may arise from
Volume 3 Issue 3 (2025) 5 doi: 10.36922/bh.6683