Page 16 - BH-3-3
P. 16
Brain & Heart Advances in stroke treatment
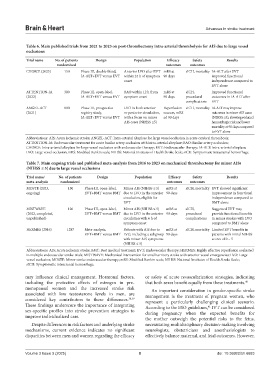
Table 6. Main published trials from 2021 to 2023 on post‑thrombectomy intra‑arterial thrombolysis for AIS due to large vessel
occlusions
Trial name No. of patients Design Population Efficacy Safety Results
randomized outcomes outcomes
CHOICE (2023) 150 Phase III, double-blind, Anterior LVO after EVT mRS at sICH, mortality IA-ALT after EVT
IA-ALT+EVT versus EVT within 24 h of symptom 90 days improved functional
onset independence compared to
EVT alone
ATTENTION-IA 300 Phase III, open-label, BAO within 12 h from mRS at sICH, Improved functional
(2022) IA-ALT+EVT versus EVT symptom onset 90 days procedural outcomes in IA-ALT after
complications EVT
ANGEL-ACT 800 Phase III, prospective LVO in both anterior Reperfusion sICH, mortality IA-ALT may improve
(2021) registry study, or posterior circulation, success, mRS outcomes in minor AIS cases
IA-ALT+EVT versus EVT with a focus on minor ad 90 days (NIHSS ≤5), showing reduced
AIS cases (NIHSS ≤5) hemorrhagic risk and lower
mortality at 90 days compared
to EVT alone
Abbreviations: AIS: Acute ischemic stroke; ANGEL-ACT: Intra-arterial alteplase for large vessel occlusion in acute cerebral thrombosis;
ATTENTION-IA: Endovascular treatment for acute basilar artery occlusion with intra-arterial alteplase; BAO: Basilar artery occlusion;
CHOICE: Intra-arterial alteplase for large vessel occlusion with endovascular therapy; EVT: Endovascular therapy; IA-ALT: Intra-arterial alteplase;
LVO: Large vessel occlusion; mRS: Modified Rankin scale; NIHSS: National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale; sICH: Symptomatic intracranial hemorrhage.
Table 7. Main ongoing trials and published meta‑analysis from 2016 to 2023 on mechanical thrombectomy for minor AISs
(NIHSS ≤ 5) due to large vessel occlusions
Trial name/ No. of patients Design Population Efficacy Safety Results
meta‑analysis randomized outcomes outcomes
MOSTE (2023, 150 Phase III, open-label, Minor AIS (NIHSS ≤ 5) mRS at sICH, mortality EVT showed significant
ongoing) EVT+BMT versus BMT due to LVO in the anterior 90 days improvement in functional
circulation, eligible for independence compared to
EVT BMT alone
MISTWAVE 120 Phase III, open-label, Minor AIS (NIHSS ≤ 5) mRS at sICH, Suggested EVT may
(2022, completed, EVT+BMT versus BMT due to LVO in the anterior 90 days procedural provide functional benefits
unpublished) circulation with 6 h of complications in minor strokes with LVO
symptom onset compared to BMT alone
HERMES (2016) 1287 Meta-analysis, Patients with AIS due to mRS at sICH, mortality Limited EVT benefits in
EVT+BMT versus BMT LVO, including a subgroup 90 days patients with initial NIHSS
with minor AIS symptoms scores of 0 – 5
(NIHSS ≤ 5)
Abbreviations: AIS: Acute ischemic stroke; BMT: Best medical treatment; EVT: Endovascular therapy; HERMES: Highly effective reperfusion evaluated
in multiple endovascular stroke trials; MISTWAVE: Mechanical intervention for small territory stroke with anterior vessel emergencies; LVO: Large
vessel occlusion; MOSTE: Minor stroke endovascular therapy; mRS: Modified Rankin scale; NIHSS: National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale;
sICH: Symptomatic intracranial hemorrhage.
may influence clinical management. Hormonal factors, or safety of acute revascularization strategies, indicating
including the protective effects of estrogen in pre- that both sexes benefit equally from these treatments. 40
menopausal women and the increased stroke risk An important consideration in gender-specific stroke
associated with low testosterone levels in men, are management is the treatment of pregnant women, who
considered key contributors to these differences. 38,39 represent a particularly challenging clinical scenario.
These findings underscore the importance of integrating According to the ESO guidelines, IVT can be considered
41
sex-specific profiles into stroke prevention strategies to during pregnancy when the expected benefits for
improve individualized care. the mother outweigh the potential risks to the fetus,
Despite differences in risk factors and underlying stroke necessitating multidisciplinary decision-making involving
mechanisms, current evidence indicates no significant neurologists, obstetricians and anesthesiologists to
disparities between men and women regarding the efficacy effectively balance maternal, and fetal outcomes. However,
Volume 3 Issue 3 (2025) 8 doi: 10.36922/bh.6683