Page 144 - EJMO-9-1
P. 144
Eurasian Journal of Medicine and
Oncology
Machine learning insights into heart failure outcomes
adverse outcomes in HF. The comprehensive assessment likelihood of death events. Furthermore, the matrix
of attribute importance provides valuable insights for highlights the presence of both positive and negative
clinicians and researchers alike, facilitating risk assessment correlations among various attributes. For example, there
and personalized care for HF patients. Further validation is a positive correlation between serum sodium levels and
and exploration of these findings are warranted to enhance ejection fraction (correlation coefficient = 0.176), while a
prognostic models and improve patient outcomes. negative correlation exists between serum creatinine levels
and serum sodium levels (correlation coefficient = −0.189).
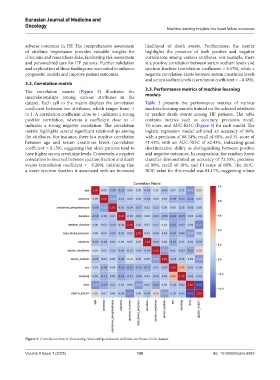
3.2. Correlation matrix
The correlation matrix (Figure 2) illustrates the 3.3. Performance metrics of machine learning
interrelationships among various attributes in the models
dataset. Each cell in the matrix displays the correlation Table 3 presents the performance metrics of various
coefficient between two attributes, which ranges from -1 machine learning models trained on the selected attributes
to 1. A correlation coefficient close to 1 indicates a strong to predict death events among HF patients. The table
positive correlation, whereas a coefficient close to -1 contains metrics such as accuracy, precision, recall,
indicates a strong negative correlation. The correlation F1-score, and AUC-ROC (Figure 3) for each model. The
matrix highlights several significant relationships among logistic regression model achieved an accuracy of 80%,
the attributes. For instance, there is a positive correlation with a precision of 88.24%, recall of 60%, and F1-score of
between age and serum creatinine levels (correlation 71.43%, with an AUC-ROC of 83.43%, indicating good
coefficient = 0.159), suggesting that older patients tend to discriminative ability in distinguishing between positive
have higher serum creatinine levels. Conversely, a negative and negative outcomes. In comparison, the random forest
correlation is observed between ejection fraction and death classifier demonstrated an accuracy of 73.33%, precision
events (correlation coefficient = −0.269), indicating that of 80%, recall of 48%, and F1-score of 60%. The AUC-
a lower ejection fraction is associated with an increased ROC value for this model was 84.17%, suggesting robust
Figure 2. Correlation matrix illustrating relationships between different attributes in the dataset
Volume 9 Issue 1 (2025) 136 doi: 10.36922/ejmo.6583