Page 180 - EJMO-9-2
P. 180
Eurasian Journal of
Medicine and Oncology PD-1/L1 inhibitors in advanced CC: Multicenter retro
and no substantial disparities in clinical characteristics In a univariate analysis using the Cox regression model,
were observed. Confounding factors were accounted for in the use of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors in first-line therapy was
the subsequent analysis. associated with better PFS (hazard ratio = 0.43, 95% CI
0.30 – 0.61, Table 2). While the other factors, including
3.2. The effects of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors on PFS histology (p=0.73), patient age (p=0.74), surgery (p=0.08),
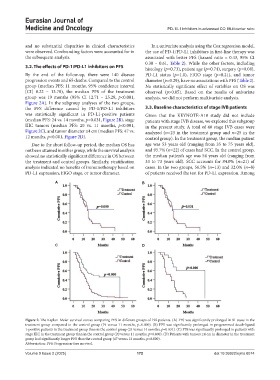
By the end of the follow-up, there were 140 disease PD-L1 status (p=1.0), FIGO stage (p=0.21), and tumor
progression events and 65 deaths. Compared to the control diameter (p=0.29), have no associations with PFS (Table 2).
group (median PFS: 11 months, 95% confidence interval No statistically significant effect of variables on OS was
[CI] 8.22 – 13.78), the median PFS of the treatment observed (p>0.05). Based on the results of univariate
group was 19 months (95% CI 12.71 – 25.29, p<0.001, analysis, we did not perform multivariate analysis.
Figure 2A). In the subgroup analyses of the two groups,
the PFS difference caused by PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors 3.3. Baseline characteristics of stage IVB patients
was statistically significant in PD-L1-positive patients Given that the KEYNOTE-A18 study did not include
(median PFS: 24 vs. 14 months, p=0.031, Figure 2B), stage patients with stage IVB disease, we explored this subgroup
IIIC tumors (median PFS: 20 vs. 11 months, p<0.001, in the present study. A total of 48 stage IVB cases were
Figure 2C), and tumor diameter ≤4 cm (median PFS: 47 vs. analyzed (n=23 in the treatment group and n=25 in the
12 months, p<0.001, Figure 2D). control group). In the treatment group, the median patient
Due to the short follow-up period, the median OS has age was 53 years old (ranging from 35 to 75 years old),
not been attained in either group, while the survival analysis and 95.7% (n=22) of cases had SCC. In the control group,
showed no statistically significant difference in OS between the median patient’s age was 54 years old (ranging from
the treatment and control groups. Similarly, stratification 33 to 73 years old). SCC accounts for 84.0% (n=21) of
analysis indicated no benefits of immunotherapy based on cases. In the two groups, 56.5% (n=13) and 32.0% (n=8)
PD-L1 expression, FIGO stage, or tumor diameter. of patients received the test for PD-L1 expression. Among
A B
C D
Figure 2. The Kaplan–Meier survival curves comparing PFS in different groups of 192 patients. (A) PFS was significantly prolonged in 91 cases in the
treatment group compared to the control group (19 versus 11 months, p=0.000). (B) PFS was significantly prolonged in programmed death-ligand
1-positive patients in the treatment group than in the control group (24 versus 14 months, p=0.031). (C) PFS was significantly prolonged in patients with
stage IIIC in the treatment group than in the control group (20 versus 11 months, p=0.000). (D) Patients with tumors ≤4 cm in diameter in the treatment
group had significantly longer PFS than the control group (47 versus 12 months, p=0.000).
Abbreviation: PFS: Progression-free survival.
Volume 9 Issue 2 (2025) 172 doi:10.36922/ejmo.8074