Page 73 - EJMO-9-2
P. 73
Eurasian Journal of
Medicine and Oncology Gut microbiota and hyperuricemia: Mechanisms and therapeutic strategies
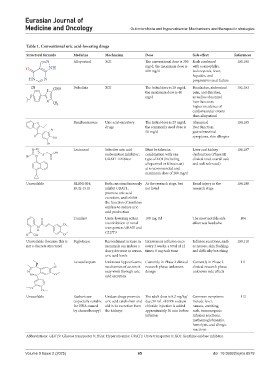
Table 1. Conventional uric acid‑lowering drugs
Structural formula Medicine Mechanism Dose Side effect References
Allopurinol XOI The conventional dose is 300 Rash combined 100,101
mg/d; the maximum dose is with eosinophilia,
600 mg/d leukocytosis, fever,
hepatitis, and
progressive renal failure
Feibulista XOI The initial dose is 20 mg/d; Headaches, abdominal 102,103
the maximum dose is 40 pain, and diarrhea,
mg/d as well as abnormal
liver function;
higher incidence of
cardiovascular events
than allopurinol
Benzbromarone Uric acid-excretory The initial dose is 25 mg/d; Abnormal 104,105
drugs the commonly used dose is liver function,
50 mg/d gastrointestinal
symptoms, skin allergies
Lesinurad Selective uric acid Must be taken in Liver and kidney 106,107
reabsorption inhibitor; combination with one dysfunction (Phase III
URAT1 inhibitor type of XOI (including clinical trial; overall safe
allopurinol or febuxostat) and well tolerated)
at a recommended and
maximum dose of 200 mg/d
Unavailable RLBN1001; Both can simultaneously At the research stage, but Renal injury in the 104,108
KUX-1511 inhibit URAT1, not listed research stage
promote uric acid
excretion, and inhibit
the function of xanthine
oxidase to reduce uric
acid production
Tranilast Urate-lowering action 100 mg, tid The most notable side 104
via inhibition of renal effect was headache
transporters URATl and
GLUT9
Unavailable (because this is Pegloticase Recombinant uricase in Intravenous infusion once Infusion reactions, such 109,110
not a discrete structure) mammals can induce a every 2 weeks; a total of 12 as nausea, skin flushing,
sharp decrease in serum times; 8 mg each time and difficulty breathing
uric acid levels
Levotofisopam Unknown hypouricemic Currently in Phase 2 clinical Currently in Phase 2 111
mechanism of action; it research phase; unknown clinical research phase;
may work through uric dosage unknown side effects
acid excretion
Unavailable Rasburicase Uridase drugs promote The adult dose is 0.2 mg/kg/ Common symptoms 112
(especially suitable uric acid catabolism and day; 50 mL of 0.9% sodium include fever,
for HUA caused aid in its excretion from chloride injection is added nausea, vomiting,
by chemotherapy) the kidneys approximately 30 min before rash, immunogenic
infusion infusion reactions,
methemoglobinemia,
hemolysis, and allergic
reactions
Abbreviations: GLUT9: Glucose transporter 9; HUA: Hyperuricemia; URAT1: Urate transporter 1; XOI: Xanthine oxidase inhibitor.
Volume 9 Issue 2 (2025) 65 doi: 10.36922/ejmo.8579