Page 113 - EJMO-9-3
P. 113
Eurasian Journal of
Medicine and Oncology Vitamin D and breast cancer
was found by MR-Egger intercept and MR-PRESSO
analysis. In the screening of instrumental variables, a strict
selection criterion (p<5 × 10 ) was adopted, the linkage
−8
disequilibrium parameter (r ) threshold was set at 0.001,
2
and the genetic distance was set at 10,000 kb to reduce the
risk of weak instrumental variables. In addition, the results
were consistent with previous studies through further
analysis of the stay-one-method method, thus confirming
the robustness and reliability of the conclusions of this
study. R software (version 4.2.2) and two software packages,
TwoSampleMR (version 0.5.6) and MR-PRESSO, were
used in this study. To address weak instrument bias and
pleiotropy, we conducted complementary MR-robust
adjusted profile score analyses (p=0.77, OR = 1.01, 95%
CI: 0.94 – 1.09) and MR-least absolute shrinkage and
selection operator (OR = 1.00, 95% CI: 0.91 – 1.10), which
yielded consistent null associations.
3. Results
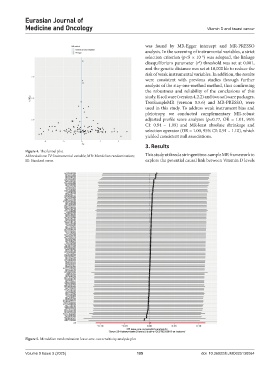
Figure 4. The funnel plot
Abbreviations: IV: Instrumental variable; MR: Mendelian randomization; This study utilized a stringent two-sample MR framework to
SE: Standard error. explore the potential causal link between Vitamin D levels
Figure 5. Mendelian randomization leave-one-out sensitivity analysis plot
Volume 9 Issue 3 (2025) 105 doi: 10.36922/EJMO025130064