Page 158 - EJMO-9-3
P. 158
Eurasian Journal of
Medicine and Oncology Pfannenstiel incision in endometrial cancer
incision is well-established in gynecologic surgery, offering
favorable cosmetic outcomes, reduced postoperative pain,
and a lower risk of wound complications when compared to
vertical midline incisions. Several studies have highlighted
that this approach can provide sufficient access to the
pelvic cavity while minimizing trauma to the abdominal
wall, potentially resulting in decreased rates of surgical
site infection and incisional hernia, particularly in obese
patients. Furthermore, the incision’s location along natural
skin folds contributes to improved patient satisfaction and
faster return to daily activities. 22,23 Laparoscopy plays an
important role in the surgical treatment of EC. However,
24
it may not be suitable for every patient. In some cases,
laparotomy may be more advantageous than laparoscopy.
We prefer laparotomy over laparoscopy in patients with
vaginal stenosis, morbid obesity that precludes safe trocar
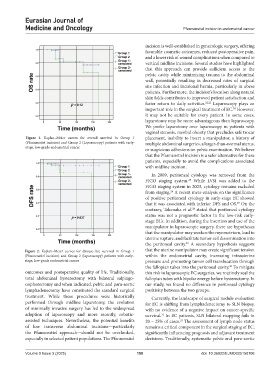
Figure 1. Kaplan–Meier curves for overall survival in Group 1 placement, inability to insert a manipulator, a history of
(Pfannenstiel incision) and Group 2 (Laparoscopy) patients with early- multiple abdominal surgeries, a larger-than-normal uterus,
stage, low-grade endometrial cancer
or suspicious adhesions on pelvic examination. We believe
that the Pfannenstiel incision is a safer alternative for these
patients, especially to avoid the complications associated
with midline incision.
In 2009, peritoneal cytology was removed from the
FIGO staging system. While LVSI was added to the
25
FIGO staging system in 2023, cytology remains excluded
from staging. A recent meta-analysis on the significance
26
of positive peritoneal cytology in early-stage EC showed
that it was associated with inferior DFS and OS. On the
27
contrary, Takenaka et al. stated that peritoneal cytology
28
status was not a prognostic factor in the low-risk early-
stage ECs. In addition, during the insertion and use of the
manipulator in laparoscopic surgery, there are hypotheses
that the manipulator may weaken the myometrium, lead to
uterine rupture, and facilitate tumor cell dissemination into
the peritoneal cavity. A secondary hypothesis suggests
29
Figure 2. Kaplan–Meier curves for disease-free survival in Group 1 that the uterine manipulator may create significant tension
(Pfannenstiel incision) and Group 2 (laparoscopy) patients with early- within the endometrial cavity, increasing intrauterine
stage, low-grade endometrial cancer pressure and promoting tumor cell translocation through
the fallopian tubes into the peritoneal cavity. To mitigate
30
outcomes and postoperative quality of life. Traditionally, this risk in laparoscopic EC surgeries, we routinely seal the
total abdominal hysterectomy with bilateral salpingo- fallopian tubes with bipolar energy before hysterectomy. In
oophorectomy and when indicated, pelvic and para-aortic our study, we found no difference in peritoneal cytology
lymphadenectomy have constituted the standard surgical positivity between the two groups.
treatment. While these procedures were historically Currently, the landscape of surgical nodule evaluation
performed through midline laparotomy, the evolution for EC is shifting from lymphadenectomy to SLN biopsy,
of minimally invasive surgery has led to the widespread with no evidence of a negative impact on cancer-specific
adoption of laparoscopy and more recently, robotic- survival. In EC patients, SLN bilateral mapping fails in
31
assisted techniques. Nevertheless, the potential benefits 20 – 25% of cases. The assessment of lymph node status
32
of low transverse abdominal incisions—particularly remains a critical component in the surgical staging of EC,
the Pfannenstiel approach—should not be overlooked, significantly influencing prognosis and adjuvant treatment
especially in selected patient populations. The Pfannenstiel decisions. Traditionally, systematic pelvic and para-aortic
Volume 9 Issue 3 (2025) 150 doi: 10.36922/EJMO025150106