Page 30 - EJMO-9-3
P. 30
Eurasian Journal of
Medicine and Oncology Role of common CXC chemokines in NAFLD
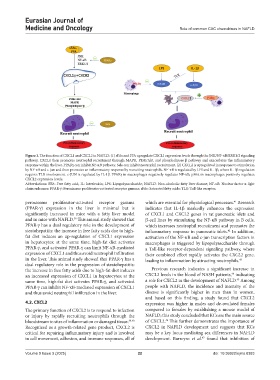
Figure 1. The function of CXCL1 and CXCL2 in NAFLD: (1) sFAs and FFA upregulate CXCL1 expression levels through the JNK/NF-κB/ERK1/2 signaling
pathway. CXCL1 then promotes neutrophil recruitment through MAPK, PI3K/Akt, and phospholipase β pathway and exacerbates the inflammatory
response within the liver. PPARγ can inhibit NF-κB pathway; Sele can inhibit neutrophil recruitment. (2) CXCL2 is upregulated in response to stimulation
by NF-κB and c-jun and then promotes an inflammatory response by recruiting neutrophils. NF-κB is regulated by LPS and IL-1β, where IL-1β regulation
requires TLR involvement. c-JUN is regulated by IL-1β. PPARγ in macrophages negatively regulates NF-κB; p38α in macrophages positively regulates
CXCL2 expression levels.
Abbreviations: FFA: Free fatty acid; IL: Interleukin; LPS: Lipopolysaccharide; NAFLD: Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; NF-κB: Nuclear factor κ light
chain enhancer; PPAR-γ: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma; sFAs: Saturated fatty acids; TLR: Toll-like receptor.
41
peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma which are essential for physiological processes. Research
(PPAR-γ) expression in the liver is minimal but is indicates that IL-1β markedly enhances the expression
significantly increased in mice with a fatty liver model of CXCL1 and CXCL2 genes in rat pancreatic islets and
38
and in mice with NAFLD. This animal study showed that β-cell lines by stimulating the NF-κB pathway in B cells,
PPAR-γ has a dual regulatory role in the development of which increases neutrophil recruitment and promotes the
steatohepatitis: the increase in free fatty acids due to high- inflammatory response in pancreatic islets. In addition,
42
fat diet induces an up-regulation of CXCL1 expression activation of the NF-κB and c-jun transcription factors in
in hepatocytes; at the same time, high-fat diet activates macrophages is triggered by lipopolysaccharide through
PPAR-γ, and activated PPAR-γ can limit NF-κB-mediated a Toll-like receptor-dependent signaling pathway, where
expression of CXCL1 and thus avoid neutrophil infiltration their combined effect rapidly activates the CXCL2 gene,
in the liver. This animal study showed that PPAR-γ has a leading to inflammation by attracting neutrophils. 43
dual regulatory role in the progression of steatohepatitis:
the increase in free fatty acids due to high-fat diet induces Previous research indicates a significant increase in
44
an increased expression of CXCL1 in hepatocytes; at the CXCL2 levels in the blood of NASH patients, indicating
45
same time, high-fat diet activates PPAR-γ, and activated a role for CXCL2 in the development of NAFLD. Among
PPAR-γ can inhibit NF-κB-mediated expression of CXCL1 people with NAFLD, the incidence and intensity of the
and thus avoid neutrophil infiltration in the liver. disease is significantly higher in men than in women,
and based on this finding, a study found that CXCL2
4.2. CXCL2 expression was higher in males and de-ovulated females
The primary function of CXCL2 is to respond to infection compared to females by establishing a mouse model of
or injury by rapidly recruiting neutrophils through the NAFLD; this study concluded that KCs are the main source
46
bloodstream to sites of inflammation or damaged tissue. 39,40 of CXCL2. This further demonstrates the importance of
Recognized as a growth-related gene product, CXCL2 is CXCL2 in NAFLD development and suggests that KCs
critical for repairing inflammatory injury and is involved may be a key locus mediating sex differences in NAFLD
in cell movement, adhesion, and immune responses, all of development. Barreyro et al. found that inhibition of
47
Volume 9 Issue 3 (2025) 22 doi: 10.36922/ejmo.8383