Page 76 - EJMO-9-3
P. 76
Eurasian Journal of
Medicine and Oncology Molecular shift in FLT3 during AML course
Table 1. Summary of included studies
Study Year of Number Mutation (s) References
publication of evaluated
patients
Kottaridis et al. 2002 44 FLT3-ITD; 26
FLT3-TKD
Nakamura et al. 2004 24 FLT3-ITD; 27
FLT3-TKD
Tiesmeier et al. 2004 31 FLT3-ITD; 28
FLT3-TKD
Suzuki et al. 2005 39 FLT3-ITD; 29
FLT3-TKD
Cloos et al. 2006 38 FLT3-ITD; 30
FLT3-TKD
Palmisano et al. 2007 28 FLT3-ITD; 31
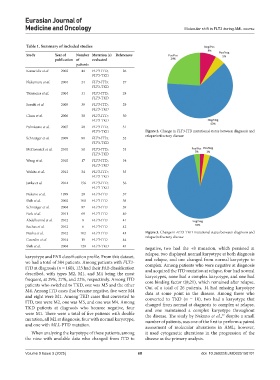
FLT3-TKD Figure 2. Change in FLT3-ITD mutational status between diagnosis and
relapse/refractory disease
Schnittger et al. 2009 80 FLT3-ITD; 32
FLT3-TKD
McCormick et al. 2010 50 FLT3-ITD; 33
FLT3-TKD
Wang et al. 2010 17 FLT3-ITD; 34
FLT3-TKD
Wakita et al. 2012 34 FLT3-ITD; 35
FLT3-TKD
Janke et al. 2014 156 FLT3-ITD; 36
FLT3-TKD
Nakano et al. 1999 28 FLT3-ITD 37
Shih et al. 2002 108 FLT3-ITD 38
Schnittger et al. 2004 97 FLT3-ITD 39
Park et al. 2011 69 FLT3-ITD 40
Abdelhamid et al. 2012 8 FLT3-ITD 41
Bachas et al. 2012 6 FLT3-ITD 42
Nazha et al. 2012 102 FLT3-ITD 43 Figure 3. Change in FLT3-TKD mutational status between diagnosis and
relapse/refractory disease
Gourdin et al. 2014 15 FLT3-ITD 44
Shih et al. 2004 120 FLT3-TKD 45 negative, two had the +8 mutation, which persisted at
relapse, two displayed normal karyotype at both diagnosis
karyotype and FAB classification profile. From this dataset, and relapse, and one changed from normal karyotype to
we had a total of 384 patients. Among patients with FLT3- complex. Among patients who were negative at diagnosis
ITD at diagnosis (n = 160), 123 had their FAB classification and acquired the ITD mutation at relapse, four had normal
described, with types M2, M1, and M4 being the most karyotypes, none had a complex karyotype, and one had
frequent, at 29%, 27%, and 22%, respectively. Among ITD core binding factor t(8;21), which remained after relapse.
patients who switched to TKD, one was M5 and the other Out of a total of 26 patients, 14 had missing karyotype
M4. Among ITD cases that became negative, five were M4 data at some point in the disease. Among those who
and eight were M1. Among TKD cases that converted to converted to TKD (n = 10), two had a karyotype that
ITD, two were M2, one was M5, and one was M4. Among changed from normal at diagnosis to complex at relapse,
TKD patients at diagnosis who became negative, four and one maintained a complex karyotype throughout
were M1. There were a total of five patients with double the disease. The study by Nakano et al., despite a small
37
mutation, all M2 at diagnosis, four with normal karyotype, number of patients, was one of the first to perform a paired
and one with MLL-PTD mutation. assessment of molecular alterations in AML; however,
When analyzing the karyotype of these patients, among it used cytogenetic alterations in the progression of the
the nine with available data who changed from ITD to disease as the primary analysis.
Volume 9 Issue 3 (2025) 68 doi: 10.36922/EJMO025150101