Page 133 - GHES-3-1
P. 133
Global Health Economics and
Sustainability
Adherence to ART among HIV patients in Cameroon
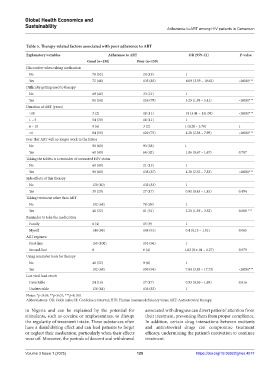
Table 5. Therapy‑related factors associated with poor adherence to ART
Explanatory variables Adherence to ART OR (95% CI) P‑value
Good (n=150) Poor (n=159)
Discomfort when taking medication
No 78 (52) 24 (15) 1
Yes 72 (48) 135 (85) 6.09 (3.59 – 10.62) <0.001***
Difficulty getting used to therapy
No 69 (46) 33 (21) 1
Yes 81 (54) 126 (79) 3.25 (1.98 – 5.41) <0.001***
Duration of ART (years)
>10 3 (2) 18 (11) 18 (3.41 – 131.08) <0.001***
1 – 5 54 (36) 18 (11) 1
6 – 10 9 (6) 3 (2) 1 (0.20 – 3.78) 1
<1 84 (56) 120 (75) 4.28 (2.38 – 7.99) <0.001***
Fear that ART will no longer work in the future
No 90 (60) 93 (58) 1
Yes 60 (40) 66 (42) 1.06 (0.67 – 1.67) 0.787
Taking the tablets is a reminder of unwanted HIV status
No 60 (40) 21 (13) 1
Yes 90 (60) 138 (87) 4.38 (2.52 – 7.83) <0.001***
Side effects of this therapy
No 120 (80) 132 (83) 1
Yes 30 (20) 27 (17) 0.81 (0.45 – 1.45) 0.494
Taking treatment other than ART
No 102 (68) 78 (49) 1
Yes 48 (32) 81 (51) 2.20 (1.39 – 3.52) 0.008 ***
Reminder to take the medication
Family 6 (4) 15 (9) 1
Myself 144 (96) 144 (91) 0.4 (0.13 – 1.01) 0.065
ART regimen
First-line 150 (100) 153 (96) 1
Second-line 0 6 (4) 1.02 (8.e-01 – 1.27) 0.979
Using reminder tools for therapy
No 48 (32) 9 (6) 1
Yes 102 (68) 150 (94) 7.84 (3.85 – 17.73) <0.001***
Last viral load result
Detectable 24 (16) 27 (17) 0.93 (0.50 – 1.69) 0.816
Undetectable 126 (84) 132 (83) 1
Notes: *p<0.05; **p<0.01; ***p<0.001.
Abbreviations: OR: Odds ratio; CI: Confidence interval; HIV: Human immunodeficiency virus; ART: Antiretroviral therapy.
in Nigeria and can be explained by the potential for associated with drug use can divert patients’ attention from
stimulants, such as cocaine or amphetamines, to disrupt their treatment, preventing them from proper compliance.
the regularity of treatment intake. These substances often In addition, certain drug interactions between excitants
have a disinhibiting effect and can lead patients to forget and antiretroviral drugs can compromise treatment
or neglect their medication, particularly when their effects efficacy, undermining the patient’s motivation to continue
wear off. Moreover, the periods of descent and withdrawal treatment.
Volume 3 Issue 1 (2025) 125 https://doi.org/10.36922/ghes.4077