Page 56 - GHES-3-2
P. 56
Global Health Economics and
Sustainability
Aging and health facilities in Indian cities
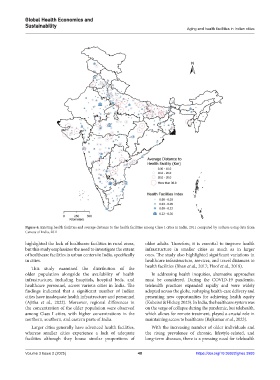
Figure 6. Existing health facilities and average distance to the health facilities among Class I cities in India, 2011 computed by authors using data from
Census of India, 2011
highlighted the lack of healthcare facilities in rural areas, older adults. Therefore, it is essential to improve health
but this study emphasizes the need to investigate the extent infrastructure in smaller cities as much as in larger
of healthcare facilities in urban centers in India, specifically ones. The study also highlighted significant variations in
in cities. healthcare infrastructure, services, and travel distances to
This study examined the distribution of the health facilities (Bhan et al., 2017; Hoof et al., 2018).
older population alongside the availability of health In addressing health inequities, alternative approaches
infrastructure, including hospitals, hospital beds, and must be considered. During the COVID-19 pandemic,
healthcare personnel, across various cities in India. The telehealth practices expanded rapidly and were widely
findings indicated that a significant number of Indian adopted across the globe, reshaping health-care delivery and
cities have inadequate health infrastructure and personnel presenting new opportunities for achieving health equity
(Ajitha et al., 2022). Moreover, regional differences in (Kobeissi & Hickey, 2023). In India, the healthcare system was
the concentration of the older population were observed on the verge of collapse during the pandemic, but telehealth,
among Class I cities, with higher concentrations in the which allows for remote treatment, played a crucial role in
northern, southern, and eastern parts of India. maintaining access to healthcare (Rajkumar et al., 2023).
Larger cities generally have advanced health facilities, With the increasing number of older individuals and
whereas smaller cities experience a lack of adequate the rising prevalence of chronic, lifestyle-related, and
facilities although they house similar proportions of long-term diseases, there is a pressing need for telehealth
Volume 3 Issue 2 (2025) 48 https://doi.org/10.36922/ghes.3993