Page 67 - GHES-3-2
P. 67
Global Health Economics and
Sustainability
Implementation of payment exemption in Cameroon
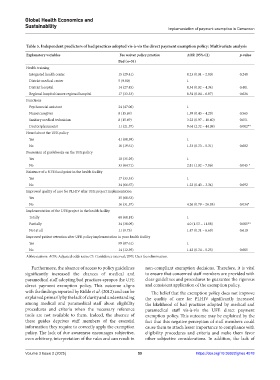
Table 5. Independent predictors of bad practices adopted vis‑à‑vis the direct payment exemption policy: Multivariate analysis
Explanatory variables Fee waiver policy practice AOR (95% CI) p‑value
Bad (n=51)
Health training
Integrated health center 15 (29.41) 0.23 (0.01 – 2.80) 0.248
District medical center 5 (9.80) 1
District hospital 14 (27.45) 0.34 (0.02 – 4.34) 0.401
Regional hospital/annex regional hospital 17 (33.33) 0.54 (0.04 – 6.87) 0.626
Functions
Psychosocial assistant 24 (47.06) 1
Nurse/caregiver 8 (15.69) 1.39 (0.43 – 4.29) 0.565
Sanitary medical technician 8 (15.69) 3.22 (0.97 – 10.60) 0.051
Doctor/pharmacist 11 (21.57) 9.64 (2.32 – 44.09) 0.002**
Heard about the UFE policy
Yes 41 (80.39) 1
No 10 (19.61) 1.33 (0.33 – 5.31) 0.682
Possession of guidebooks on the UFE policy
Yes 18 (35.29) 1
No 33 (64.71) 2.81 (1.02 – 7.86) 0.045 *
Existence of a UFE focal point in the health facility
Yes 17 (33.33) 1
No 34 (66.67) 1.22 (0.43 – 3.34) 0.692
Improved quality of care for PLHIV after UFE project implementation
Yes 35 (68.63)
No 16 (31.37) 4.26 (0.79 – 26.95) 0.034*
Implementation of the UFE project in the health facility
Totally 68 (60.18) 1
Partially 34 (30.09) 4.0 (1.53 – 11.08) 0.005**
Not at all 11 (9.73) 1.47 (0.31 – 6.69) 0.610
Improved patient retention after UFE policy implementation in your health facility
Yes 99 (87.61) 1
No 14 (12.39) 1.42 (0.34 – 5.25) 0.605
Abbreviations: AOR: Adjusted odds ratio; CI: Confidence interval; UFE: User fees elimination.
Furthermore, the absence of access to policy guidelines non-compliant exemption decisions. Therefore, it is vital
significantly increased the chances of medical and to ensure that concerned staff members are provided with
paramedical staff adopting bad practices apropos the UFE clear guidelines and procedures to guarantee the rigorous
direct payment exemption policy. This outcome aligns and consistent application of the exemption policy.
with the findings reported by Ridde et al. (2012) and can be The belief that the exemption policy does not improve
explained primarily by the lack of clarity and understanding the quality of care for PLHIV significantly increased
among medical and paramedical staff about eligibility the likelihood of bad practices adopted by medical and
procedures and criteria when the necessary reference paramedical staff vis-à-vis the UFE direct payment
tools are not available to them. Indeed, the absence of exemption policy. This outcome may be explained by the
these guides deprives staff members of the essential fact that this negative perception of staff members could
information they require to correctly apply the exemption cause them to attach lesser importance to compliance with
policy. The lack of due awareness encourages subjective, eligibility procedures and criteria and make them favor
even arbitrary, interpretation of the rules and can result in other subjective considerations. In addition, the lack of
Volume 3 Issue 2 (2025) 59 https://doi.org/10.36922/ghes.4078