Page 26 - GPD-2-4
P. 26
Gene & Protein in Disease The roles and mechanisms of ETS1 in diseases
phosphorylation stability of the ETS1 core in the SRR Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) have been shown to
region . regulate the development of cancer in numerous studies.
[50]
Recently, Jin et al. reported that ETS1 promotes the
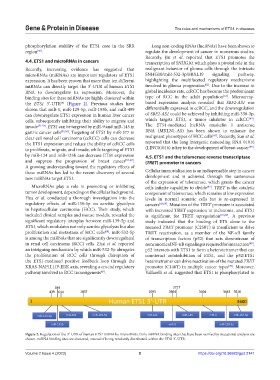
4.4. ETS1 and microRNAs in cancers transcription of SNHG10, which plays a pivotal role in the
Recently, increasing evidence has suggested that malignant behavior of glioma cells through the intricate
microRNAs (miRNAs) are important regulators of ETS1 SNHG10/miR-532-3p/FBXL19 signaling pathway,
expression. It has been proven that more than ten different highlighting the multifaceted regulatory mechanisms
[62]
miRNAs can directly target the 3’-UTR of human ETS1 involved in glioma progression . Due to the increase in
RNA to downregulate its expression. Moreover, the global incidence rate, ccRCC has become the predominant
[63]
binding sites for these miRNAs are highly clustered within type of RCC in the adult population . Microarray-
the ETS1 3’-UTR (Figure 2). Previous studies have based expression analysis revealed that SBF2-AS1 was
[9]
shown that miR-1, miR-129-5p, miR-193b, and miR-499 differentially expressed in ccRCC, and the downregulation
can downregulate ETS1 expression in human liver cancer of SBF2-AS1 could be achieved by inhibiting miR-338-3p,
[64]
cells, subsequently inhibiting their ability to migrate and which targets ETS1, a tumor inhibitor in ccRCC .
invade [51-54] . ETS1 can be targeted by miR-9 and miR-145 in The ETS1-mediated lncRNA muskelin 1 antisense
gastric cancer cells [55,56] . Targeting of ETS1 by miR-377 in RNA (MKLN1-AS) has been shown to enhance the
[65]
clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) cells can decrease malignant phenotypes of HCC cells . Recently, Sun et al.
the ETS1 expression and reduce the ability of ccRCC cells reported that the long intergenic noncoding RNA 01016
[66]
to proliferate, migrate, and invade, while targeting of ETS1 (LINC01016) is key to the development of breast cancer .
by miR-124 and miR-125b can decrease ETS1 expression 4.5. ETS1 and the telomerase reverse transcriptase
and suppress the progression of breast cancer [57-59] . (TRET) promoter in cancers
A growing understanding toward the regulatory effects of
these miRNAs has led to the recent discovery of several Cellular immortalization is an indispensable step in cancer
new miRNAs target ETS1. development and is achieved through the sustenance
of the expression of telomerase, which grants the cancer
MicroRNAs play a role in promoting or inhibiting cells infinite capability to divide . TRET is the catalytic
[67]
tumor development, depending on the cellular background. component of telomerase, which remains at low expression
Hua et al. conducted a thorough investigation into the levels in normal somatic cells but is re-expressed in
regulatory effects of miR-139-5p on aerobic glycolysis cancers [68,69] . Mutation of the TRET promoter is associated
in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Their study, which with increased TRET expression in melanoma, and ETS1
included clinical samples and mouse models, revealed the is significant for TRET upregulation [67,69] . A previous
significant regulatory interplay between miR-139-5p and study indicated that the binding of ETS alone to the
ETS1, which modulates not only aerobic glycolysis but also mutated TRET promoter (C250T) is insufficient to drive
proliferation and metastasis of HCC cells . miR-532-5p TRET reactivation, as a member of the NF-κB family
[60]
is among the miRNAs that are significantly downregulated of transcription factors (p52) that acts downstream of
in renal cell carcinoma (RCC) cells. Zhai et al. reported noncanonical NF-κB signaling is required for interaction .
[68]
an intriguing mechanism by which miR-532-5p abrogates p52 interacts with ETS1 to form a heterotetramer that can
the proliferation of RCC cells through disruption of counteract autoinhibition of ETS1, and the p52/ETS1
the ETS1-mediated positive feedback loop through the heterotetramer can drive reactivation of the mutated TRET
KRAS-NAP1L1/P-ERK axis, revealing a crucial regulatory promoter (C146T) in multiple cancer types . Moreover,
[70]
pathway involved in RCC tumorigenesis . Vallarelli et al. suggested that ETS1 is phosphorylated in
[61]
Figure 2. Regulation of the 3′-UTR of human ETS1 mRNA by microRNAs. Only miRNA binding sites that have been verified by mutational analysis are
shown. miRNA binding sites are clustered, instead of being randomly distributed, within the ETS1 3′-UTR.
Volume 2 Issue 4 (2023) 5 https://doi.org/10.36922/gpd.2141