Page 71 - GPD-3-2
P. 71
Gene & Protein in Disease Opportunities and challenges of HIF-1 in cancer
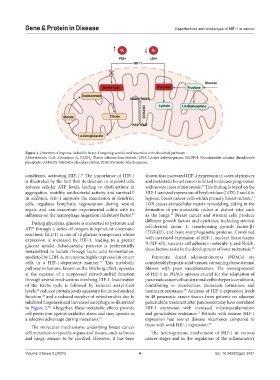
Figure 1. Overview of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 targeting aerobic and anaerobic mitochondrial pathways
Abbreviations: CoA: Coenzyme A; FADH : Flavin adenine dinucleotide; LDH: Lactate dehydrogenase; NADPH: Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide
2
phosphate; OXPHOS: Oxidative phosphorylation; PDH: Pyruvate dehydrogenase.
25
conditions, activating HIF-1. The importance of HIF-1 shown that increased HIF-1 expression in cases of primary
is illustrated by the fact that its deletion in myeloid cells and metastatic breast cancer is linked to disease progression
32
reduces cellular ATP levels, leading to dysfunctions in with severe cases of metastasis. This finding is based on the
26
aggregation, motility, antibacterial activity, and survival. HIF-1-assisted expression of lysyl oxidase (LOX) 2 and 4 in
In addition, HIF-1 supports the maturation of dendritic hypoxic breast cancer cells within primary breast tumors.
33
cells, regulates lymphatic regeneration during wound LOX causes extracellular matrix remodeling, aiding in the
repair, and can exacerbate experimental colitis with its formation of pre-metastatic niches at distant sites such
34
influence on the macrophage migration inhibitory factor. 27 as the lungs. Breast cancer and stromal cells produce
During glycolysis, glucose is converted to pyruvate and different growth factors and cytokines, including stromal
ATP through a series of oxygen-independent enzymatic cell-derived factor 1, transforming growth factor-β1
reactions. GLUT1 is one of 12 glucose transporters whose (TGF-β1), and bone morphogenetic proteins. Combined
expression is increased by HIF-1, leading to a greater with increased expression of HIF-1, nuclear factor-kappa
glucose uptake. Subsequently, pyruvate is preferentially B (NF-κB), vascular cell adhesion molecule-1, and Notch,
35
metabolized to lactate through lactic acid fermentation, these factors assist in the development of bone metastasis.
mediated by LDH-A, an enzyme highly expressed in cancer Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas (PDACs) are
15
cells in a HIF-1-dependent manner. This metabolic considerably hypoxic solid tumors, containing dense stromal
pathway in tumors, known as the Warburg effect, operates fibrosis with poor vascularization. The overexpression
at the expense of a suppressed mitochondrial function of HIF-1 in PDACs appears crucial for the adaptation of
through several mechanisms involving HIF-1. Inactivation pancreatic cancer cells and stromal cells to hypoxic conditions,
of the Krebs cycle is followed by reduced acetyl-CoA contributing to invasiveness, metastasis formation, and
28
36
levels, reduced protein levels necessary for mitochondrial treatment resistance. Analyses of HIF-1 expression levels
function, and a reduced number of mitochondria due to in 48 pancreatic cancer tissues from patients on adjuvant
29
inhibited biogenesis and increased autophagy, as illustrated gemcitabine treatment after pancreatectomy have correlated
in Figure 2. Altogether, these metabolic effects provide HIF-1 expression with increased microvascularization
30
cell protection against oxidative stress and may operate as and gemcitabine resistance. Patients with intense HIF-1
37
a selective advantage during metastasis. 31 expression had sooner disease recurrence compared to
The molecular mechanisms underlying breast cancer those with weak HIF-1 expression. 37
cell metastasis to specific organs and tissues, such as bones The heterogeneous involvement of HIF-1 in various
and lungs, remain to be clarified. However, it has been cancer stages and in the regulation of the inflammatory
Volume 3 Issue 2 (2024) 4 doi: 10.36922/gpd.3431