Page 73 - GPD-3-2
P. 73
Gene & Protein in Disease Opportunities and challenges of HIF-1 in cancer
A
B
C
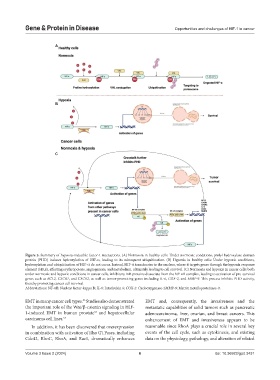
Figure 3. Summary of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 interactions. (A) Normoxia in healthy cells: Under normoxic conditions, prolyl hydroxylase domain
protein (PHD) induces hydroxylation of HIF-α, leading to its subsequent ubiquitination. (B) Hypoxia in healthy cells: Under hypoxic conditions,
hydroxylation and ubiquitination of HIF-α do not occur. Instead, HIF-α translocates to the nucleus, where it targets genes through the hypoxia response
element (HRE), affecting erythropoiesis, angiogenesis, and metabolism, ultimately leading to cell survival. (C) Normoxia and hypoxia in cancer cells: both
under normoxic and hypoxic conditions in cancer cells, inhibitory IκB proteins dissociate from the NF-κB complex, leading to activation of pro-survival
genes such as BCL2, CXCR1, and CXCR2, as well as tumor-promoting genes including IL-6, COX-2, and MMP-9. This process inhibits PHD activity,
thereby promoting cancer cell survival.
Abbreviations: NF-κB: Nuclear factor-kappa B; IL-6: Interleukin 6; COX-2: Cyclooxygenase-2MMP-9: Matrix metalloproteinase-9.
EMT in many cancer cell types. Studies also demonstrated EMT and, consequently, the invasiveness and the
53
the important role of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling in HIF- metastatic capabilities of solid tumors such as pancreatic
1-induced EMT in human prostate and hepatocellular adenocarcinoma, liver, ovarian, and breast cancers. This
54
carcinoma cell lines. 55 enhancement of EMT and invasiveness appears to be
In addition, it has been discovered that overexpression reasonable since RhoA plays a crucial role in several key
in combination with activation of Rho GTPases, including events of the cell cycle, such as cytokinesis, and existing
Cdc42, RhoC, RhoA, and Rac1, dramatically enhances data on the physiology, pathology, and alteration of related
Volume 3 Issue 2 (2024) 6 doi: 10.36922/gpd.3431