Page 25 - GPD-3-4
P. 25
Gene & Protein in Disease GLUT5 in cancer development and therapy
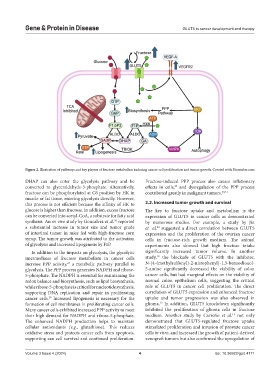
Figure 2. Illustration of pathways and key players of fructose metabolism inducing cancer cell proliferation and tumor growth. Created with Biorender.com
DHAP can also enter the glycolysis pathway and be Fructose-induced PPP process also causes inflationary
converted to glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate. Alternatively, effects in cells, and dysregulation of the PPP process
29
fructose can be phosphorylated at C6 position by HK in contributed greatly in malignant tumors. 30,31
muscle or fat tissue, entering glycolysis directly. However,
this process is not efficient because the affinity of HK to 2.2. Increased tumor growth and survival
glucose is higher than fructose. In addition, excess fructose The key to fructose uptake and metabolism is the
can be converted into acetyl-CoA, a substrate for fatty acid expression of GLUT5 in cancer cells as demonstrated
synthesis. An in vivo study by Goncalves et al. reported by numerous studies. For example, a study by Jin
26
a substantial increase in tumor size and tumor grade et al. suggested a direct correlation between GLUT5
32
of intestinal tumor in mice fed with high-fructose corn expression and the proliferation of the ovarian cancer
syrup. The tumor growth was attributed to the activation cells in fructose-rich growth medium. The animal
of glycolysis and increased lipogenesis by F1P. experiments also showed that high fructose intake
In addition to the impacts on glycolysis, the glycolytic significantly increased tumor volume. In another
10
intermediates of fructose metabolism in cancer cells study, the blockade of GLUT5 with the inhibitor,
increase PPP activity, a metabolic pathway parallel to N-[4-(methylsulfonyl)-2-nitrophenyl]-1,3-benzodioxol-
27
glycolysis. The PPP process generates NADPH and ribose- 5-amine significantly decreased the viability of colon
5-phosphate. The NADPH is essential for maintaining the cancer cells, but had marginal effects on the viability of
redox balance and biosynthesis, such as lipid biosynthesis, normal colon epithelium cells, suggesting the critical
while ribose-5-phosphate is critical for nucleotide synthesis, role of GLUT5 in cancer cell proliferation. The direct
supporting DNA replication and repair in proliferating correlation of GLUT5 expression and enhanced fructose
28
cancer cells. Increased lipogenesis is necessary for the uptake and tumor progression was also observed in
formation of cell membranes in proliferating cancer cells. glioma. In addition, GLUT5 knockdown significantly
12
Many cancer cells exhibited increased PPP activity to meet inhibited the proliferation of glioma cells in fructose
their high demand for NADPH and ribose-5-phosphate. medium. Another study by Carreño et al. not only
13
The enhanced NADPH production helps to maintain demonstrated that GLUT5-regulated fructose uptake
cellular antioxidants (e.g., glutathione). This reduces stimulated proliferation and invasion of prostate cancer
oxidative stress and protects cancer cells from apoptosis, cells in vitro, and increased the growth of patient-derived
supporting can cell survival and continued proliferation. xenograft tumors but also confirmed the upregulation of
Volume 3 Issue 4 (2024) 4 doi: 10.36922/gpd.4171