Page 95 - GPD-4-1
P. 95
Gene & Protein in Disease Oral-ERT in PD knockout mice with tobrhGAA
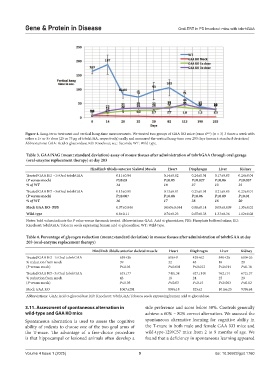
Figure 4. Long-term treatment and vertical hang-time measurements. We treated two groups of GAA KO mice (exon 6 ) (n = 3) 3 times a week with
neo
either a 1× or 3× dose (25 or 75 μg of tobrhGAA, respectively) orally and measured the vertical hang-time over 203 days (mean ± standard deviation)
Abbreviations: GAA: Acid a-glucosidase; KO: Knockout; sec.: Seconds; WT: Wild-type.
Table 3. GAA/NAG (mean±standard deviation) assay of mouse tissues after administration of tobrhGAA through oral gavage
(oral‑enzyme replacement therapy) at day 203
Hindlimb tibialis anterior Skeletal Muscle Heart Diaphragm Liver Kidney
Treated GAA KO –1×Oral tobrhGAA 0.11±0.04 0.14±0.02 0.24±0.01 0.17±0.03 0.24±0.04
(P versus mock) P≤0.05 P≤0.05 P≤0.027 P≤0.06 P≤0.037
% of WT 14 18 37 13 22
Treated GAA KO –3×Oral tobrhGAA 0.13±0.01 0.13±0.01 0.25±0.01 0.21±0.05 0.23±0.01
(P versus mock) P≤0.007 P≤0.08 P≤0.06 P≤0.09 P≤0.01
% of WT 16 17 38 16 20
Mock GAA KO‑ PBS 0.07±0.044 0.065±0.044 0.08±0.14 0.05±0.009 1.35±0.02
Wild‑type 0.8±0.11 0.76±0.23 0.65±0.38 1.33±0.36 1.12±0.08
Notes: bold values indicate the P value versus the mock treated. Abbreviations: GAA: Acid a-glucosidase; PBS: Phosphate buffered saline; KO:
Knockout; tobrhGAA: Tobacco seeds expressing human acid a-glucosidase; WT: Wild-type.
Table 4. Percentage of glycogen reduction (mean±standard deviation) in mouse tissues after administration of tobrhGAA at day
203 (oral‑enzyme replacement therapy)
Hindlimb tibialis anterior skeletal muscle Heart Diaphragm Liver Kidney
Treated GAA KO–1×Oral tobrhGAA 659±36 616±9 429±62 840±26 680±26
% reduction from mock 39 32 48 18 28
(P versus mock) P≤0.05 P≤0.001 P≤0.012 P≤0.014 P≤0.18
Treated GAA KO–3×Oral tobrhGAA 615±77 740±38 627±140 762±14 672±37
% reduction from mock 43 18 24 25 29
(P versus mock) P≤0.05 P≤0.03 P≤0.15 P≤0.003 P≤0.02
Mock GAA KO 1067±201 898±18 825±2 1016±23 939±64
Abbreviations: GAA: Acid a-glucosidase; KO: Knockout; tobrhGAA: Tobacco seeds expressing human acid a-glucosidase.
3.11. Assessment of spontaneous alternation in side preference and score below 50%. Controls generally
wild-type and GAA KO mice achieve a 60% – 80% correct alternation. We assessed the
Spontaneous alternation is used to assess the cognitive spontaneous alternative learning for cognitive ability in
ability of rodents to choose one of the two goal arms of the T-maze in both male and female GAA KO mice and
the T-maze. The advantage of a free-choice procedure wild-type-129/C57 mice from 2 to 9 months of age. We
is that hippocampal or lesioned animals often develop a found that a deficiency in spontaneous learning appeared
Volume 4 Issue 1 (2025) 9 doi: 10.36922/gpd.1760