Page 96 - GPD-4-1
P. 96
Gene & Protein in Disease Oral-ERT in PD knockout mice with tobrhGAA
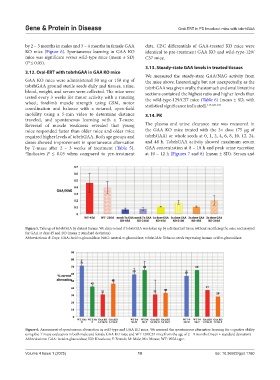
by 2 – 3 months in males and 3 – 4 months in female GAA data. CBC differentials of GAA-treated KO mice were
KO mice (Figure 6). Spontaneous learning in GAA KO identical to pre-treatment GAA KO and wild-type-129/
mice was significant versus wild-type mice (mean ± SD) C57 mice.
(P ≤ 0.05).
3.13. Steady-state GAA levels in treated tissues
3.12. Oral-ERT with tobrhGAA in GAA KO mice
We measured the steady-state GAA/NAG activity from
GAA KO mice were administered 50 mg or 150 mg of the mice above. Interestingly, but not unexpectedly, as the
tobrhGAA ground sterile seeds daily and tissues, urine, tobrhGAA was given orally, the stomach and small intestine
blood, weight, and serum were collected. The mice were sections contained the highest ratio and higher levels than
tested every 3 weeks for motor activity with a running the wild-type-129/C57 mice (Table 6) (mean ± SD, with
wheel, forelimb muscle strength using GSM, motor statistical significance indicated). 117,122-132
coordination and balance with a rotarod, open-field
mobility using a 5-min video to determine distance 3.14. PK
traveled, and spontaneous learning with a T-maze.
Reversal of muscle weakness revealed that young The plasma and urine clearance rate was measured in
mice responded faster than older mice and older mice the GAA KO mice treated with the 3× dose (75 μg of
required higher levels of tobrhGAA. Both age groups and tobrhGAA) or whole seeds at 0, 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 24,
doses showed improvement in spontaneous alternation and 48 h. TobrhGAA activity showed maximum serum
by T-maze after 2 – 3 weeks of treatment (Table 5). GAA concentration at 8 – 10 h and peak urine excretion
*Indicates P ≤ 0.05 when compared to pre-treatment at 10 – 12 h (Figures 7 and 8) (mean ± SD). Serum and
Figure 5. Take up of tobrhGAA by distant tissues. We determined if tobrhGAA was taken up by a distant tail tissue without sacrificing the mice and assayed
for GAA at days 45 and 203 (mean ± standard deviation)
Abbreviations: d: Days; GAA: Acid a-glucosidase; NAG: neutral a-glucosidase; tobrhGAA: Tobacco seeds expressing human acid a-glucosidase.
Figure 6. Assessment of spontaneous alternation in wild-type and GAA KO mice. We assessed the spontaneous alternative learning for cognitive ability
using the T-maze evaluation in both male and female GAA KO mice and WT-129/C57 mice from the age of 2 – 9 months (mean ± standard deviation)
Abbreviations: GAA: Acid a-glucosidase; KO: Knockout; F: Female; M: Male; Mo: Mouse; WT: Wild-type.
Volume 4 Issue 1 (2025) 10 doi: 10.36922/gpd.1760