Page 62 - GPD-4-2
P. 62
Gene & Protein in Disease X chromosome in sex-biased autoimmunity
are characterized by altered lymphocytic T and B cells
reactivity. ADs are complex traits, exhibiting high
1
variability across individuals. ADs arise from a breakdown
in central and peripheral self-tolerance controls leading
to the survival and proliferation of autoreactive immune
cells that cause autoimmunity. ADs include tissue/
organ-specific and systemic inflammatory disorders. It
2
is estimated that about 10% of the worldwide population
is affected by ADs, with a striking predominance among
females. ADs may be on the rise, therefore representing a
3-5
major global health and financial concern.
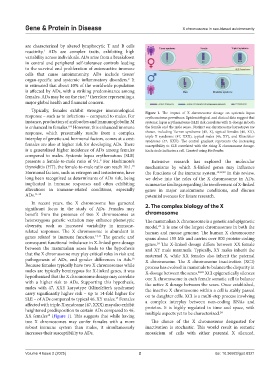
Typically, females exhibit stronger immunological Figure 1. The impact of X chromosome dosage on systemic lupus
response – such as to infections – compared to males. For erythematosus prevalence. Epidemiological and clinical data suggest that
instance, production of antibodies and immunoglobulin M systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) risk correlates with X-dosage in both
is enhanced in females. However, this enhanced immune the female and the male sexes. Distinct sex chromosome karyotypes are
6-8
response, which presumably results from a complex shown, including Turner syndrome (45, X), typical females (46, XX),
interplay of genetic and hormonal factors, comes at a cost: triple X syndrome (47, XXX), typical males (46, XY), and Klinefelter
syndrome (47, XXY). The central gradient represents the increasing
females are also at higher risk for developing ADs. There susceptibility to SLE correlated with the rising X chromosome dosage.
is a generalized higher incidence of ADs among females Each circle indicates a cell. Created using BioRender.
compared to males. Systemic lupus erythematous (SLE)
presents a female-to-male ratio of 9:1. For Hashimoto’s Extensive research has explored the molecular
9
thyroiditis (HT), the female-to-male ratio can reach 10:1. mechanisms by which X-linked genes may influence
10
Hormonal factors, such as estrogen and testosterone, have the functions of the immune system. 16,19,20 In this review,
long been recognized as determinants of ADs risk, being we delve into the roles of the X chromosome in ADs,
implicated in immune responses and often exhibiting summarize findings regarding the involvement of X-linked
alterations in immune-related conditions, especially genes in major autoimmune conditions, and discuss
ADs. 11-13 potential avenues for future research.
In recent years, the X chromosome has garnered
significant focus in the study of ADs. Females may 2. The complex biology of the X
benefit from the presence of two X chromosomes as chromosome
heterozygous genetic variation may enhance phenotypic The mammalian X chromosome is a genetic and epigenetic
diversity, such as increased variability in immune- model. It is one of the largest chromosomes in both the
21
related responses. The X chromosome is abundant in human and mouse genome. The human X chromosome
genes related to immune functions. 14,15 The genetic and spans about 155 Mb and carries over 800 protein-coding
consequent functional imbalance in X-linked gene dosage genes. The X-linked dosage differs between XX female
14
between the mammalian sexes leads to the hypothesis and XY male mammals. Typically, XY males inherit the
that the X chromosome may play critical roles in risk and maternal X, while XX females also inherit the paternal
pathogenesis of ADs, and gender differences in Ads. X chromosome. The X chromosome inactivation (XCI)
16
Because females typically have two X chromosomes while process has evolved in mammals to balance the disparity in
males are typically hemizygous for X-linked genes, it was X-dosage between the sexes. 22,23 XCI epigenetically silences
hypothesized that the X chromosome dosage may correlate one X chromosome in each female somatic cell to balance
with a higher risk to ADs. Supporting this hypothesis, the active X dosage between the sexes. Once established,
males with 47, XXY karyotype (Klinefelter’s syndrome) the inactive X chromosome within a cell is stably passed
carry significantly higher risk – up to 14-fold higher for on to daughter cells. XCI is a multi-step process involving
SLE – of ADs compared to typical 46, XY males. Females a complex interplay between non-coding RNAs and
17
affected with triple-X syndrome (47, XXX) may also exhibit proteins. It is highly regulated in time and space, with
heightened predisposition to certain ADs compared to 46, multiple aspects yet to be characterized. 24
XX females (Figure 1). This suggests that while having
18
two X chromosomes may confer females with a more The choice of the X chromosome designated for
robust immune system than males, it simultaneously inactivation is stochastic. This would result in somatic
increases their susceptibility to ADs. mosaicism of cells with either parental X silenced.
Volume 4 Issue 2 (2025) 2 doi: 10.36922/gpd.8321