Page 15 - GPD-4-3
P. 15
Gene & Protein in Disease Targeting cathepsins during cancer development
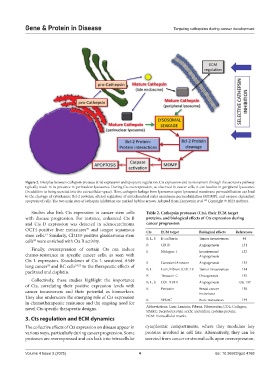
Figure 2. Interplay between cathepsin protease (Cts) expression and apoptotic regulation. Cts expression and its movement through the secretory pathway
typically result in its presence in perinuclear lysosomes. During Cts overexpression, as observed in cancer cells, it can localize in peripheral lysosomes
(in addition to being secreted into the extracellular space). Here, cathepsin leakage from lysosomes upon lysosomal membrane permeabilization can lead
to the cleavage of cytoplasmic Bcl-2 proteins, altered regulation of mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization (MOMP), and caspase-dependent
159
apoptosis of cells. The two main sites of cathepsin inhibition are marked by blue arrows. Adapted from Zamyatnin et al. Copyright © 2023 Authors.
Studies also link Cts expression in cancer stem cells Table 2. Cathepsin proteases (Cts), their ECM target
with disease progression. For instance, enhanced Cts B proteins, and biological effects of Cts expression during
and Cts D expression was detected in adenocarcinoma cancer progression
OCT4-positive liver metastases and tongue squamous Cts ECM target Biological effects References
50
51
stem cells. Similarly, CD133-positive glioblastoma stem
cells were enriched with Cts B activity. B, L, S E-cadherin Tumor invasiveness 44
52
B CD18 Angiogenesis 131
Finally, overexpression of certain Cts can induce S Nidogen-1 Invasiveness/ 132
chemo-resistance in specific cancer cells, as seen with Angiogenesis
Cts L expression. Knockdown of Cts L sensitized A549 S Canesten/Arresten Angiogenesis 133
lung cancer and BC cells 54,55 to the therapeutic effects of
53
paclitaxel and cisplatin. B, L Lam./Fibron./COL IV Tumor invasiveness 134
B Tenascin-C Oncogenesis 135
Collectively, these studies highlight the importance B, L, S COL XVIII Angiogenesis 136, 137
of Cts, correlating their positive expression levels with K Periostin Breast cancer 138
cancer invasiveness and their potential as biomarkers. metastases
They also underscore the emerging role of Cts expression K SPARC Bone metastases 139
in chemotherapeutic resistance and the ongoing need for
novel Cts-specific therapeutic designs. Abbreviations: Lam: Laminin; Fibron: Fibronectin; COL: Collagen;
SPARC: Secreted protein acidic and rich in cysteine protein;
3. Cts regulation and ECM dynamics ECM: Extracellular matrix.
The collective effects of Cts expression on disease appear in cytoplasmic compartments, where they modulate key
various ways, particularly during cancer progression. Some proteins involved in cell fate. Alternatively, they can be
proteases are overexpressed and can leak into intracellular secreted from cancer or stromal cells upon overexpression,
Volume 4 Issue 3 (2025) 4 doi: 10.36922/gpd.4768