Page 18 - GPD-4-3
P. 18
Gene & Protein in Disease Targeting cathepsins during cancer development
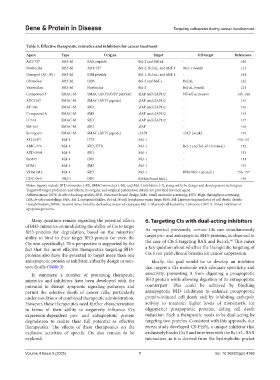
Table 3. Effective therapeutic mimetics and inhibitors for cancer treatment
Agent Type Origins Target Off‑target References
ABT-737 BH3-M BAK peptide Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL - 140
Navitoclax BH3-M ABT-737 Bcl-2, Bcl-xL, and Mcl-1 Mcl-1 (weak) 113
Gossypol (AT-101) BH3-M BIM peptide Bcl-1, Bcl-xL, and Mcl-1 - 141
Obatoclax BH3-M ISDS Bcl-2 and Mcl-1 Bcl-xL 142
Venetoclax BH3-M Navitoclax Bcl-2 Bcl-xL (weak) 121
Compound 3 SMAC-M SMAC (AVPI/AVPF peptide) xIAP and cIAP1/2 NF-κB activation 143, 144
APG1387 SMAC-M SMAC (AVPI peptide) xIAP and cIAP1/2 - 145
AT-406 SMAC-M SBD xIAP and cIAP1/2 - 146
Compound A SMAC-M SMS xIAP and cIAP1/2 - 143
LC161 SMAC-M SBD xIAP and cIAP1/2 - 147
SM-164 SMAC-M SBD xIAP - 148
Birinapant SMAC-M SMAC (AVPI peptide) cIAP1 xIAP (weak) 149
A1210477 Mcl-1 HTS Mcl-1 - 150, 151
AMG-176 Mcl-1 SBD, HTS Mcl-1 Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL (minimal) 152
AZD-5991 Mcl-1 SBD Mcl-1 - 153
S63845 Mcl-1 ISM Mcl-1 - 154
MIM1 Mcl-1 SMS Mcl-1 - 155
VU661013 Mcl-1 SBD Mcl-1 BIM-Mcl-1 (destab.) 156, 157
GDC-0941 Mcl-1 ISM PI3Kα/δ and Mcl-1 - 158
Notes: Agents include BH3-mimetics (-M), SMAC-mimetics (-M), and Mcl-1 inhibitors (-I), along with the design and development techniques.
Target/off-target protein(s) and effects, its origins, and original publication details are provided for each agent.
Abbreviations: ISDS: In silico docking studies; SBD: Structure-based design; SMS: Small molecule screening; HTS: High-throughput screening;
ISM: In silico modeling; BAK: Bcl-2 antagonist/killer; Bcl-xL: B-cell lymphoma-extra large; BIM: Bcl-2 interacting mediator of cell death; destab:
Destabilization; SMAC: Second mitochondria-derived activator of caspases; Mcl-1: Myeloid cell leukemia-1 protein; xIAP: X-linked inhibitor of
apoptosis proteins.
Many questions remain regarding the potential effects 6. Targeting Cts with dual-acting inhibitors
of BH3-mimetics on modulating the ability of Cts to target
BH3-proteins for degradation, based on the mimetics’ As reported previously, certain Cts can simultaneously
ability to bind to their target BH3-protein (or even the target pro- and antiapoptotic BH3-proteins, as observed in
86
Cts non-specifically). This perspective is supported by the the case of Cts S targeting BAX and Bcl-xL. This raises
fact that the most effective therapeutics targeting BH3- a key question about whether the therapeutic targeting of
proteins also have the potential to target more than one Cts S can yield clinical benefits for cancer suppression.
antiapoptotic protein or inhibitor, either by design or non- Ideally, the goal would be to develop an inhibitor
specifically (Table 3). that targets a Cts molecule with adequate specificity and
In summary, a number of promising therapeutic selectivity, preventing it from digesting a proapoptotic
mimetics and inhibitors have been developed with the BH3 protein while allowing digestion of its antiapoptotic
potential to disrupt apoptosis signaling pathways and counterpart. This could be achieved by blocking
permit the selective death of cancer cells, particularly antiapoptotic BH3 inhibition to enhance proapoptotic
under conditions of combined therapeutic administration. protein-induced cell death and by inhibiting cathepsin
However, these therapeutics need further characterization activity to maintain higher levels of monomeric (or
in terms of their ability to negatively influence Cts oligomeric) proapoptotic proteins, aiding cell death
expression-dependent pro- and antiapoptotic protein induction. Such a therapeutic needs to be dual-acting by
degradation to realize their full potential as effective targeting two proteins. Consistent with this approach, our
therapeutics. The effects of these therapeutics on the recent study developed CS-PEP1, a unique inhibitor that
exclusive activities of specific Cts also remain to be exclusively blocks Cts S and interferes with the Bcl-xL–BAX
explored. interaction, as it is derived from the hydrophobic pocket
Volume 4 Issue 3 (2025) 7 doi: 10.36922/gpd.4768