Page 87 - GPD-4-3
P. 87
Gene & Protein in Disease Dopaminergic dysfunction as pre-addiction
A
B
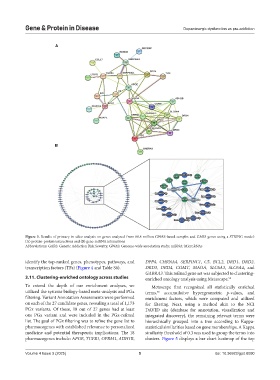
Figure 3. Results of primary in silico analysis on genes analyzed from 88.8 million GWAS-based samples and GARS genes using a STRING model:
(A) protein-protein interactions and (B) gene-miRNA interactions
Abbreviations: GARS: Genetic Addiction Risk Severity; GWAS: Genome-wide association study; miRNA: MicroRNAs
identify the top-ranked genes, phenotypes, pathways, and DPP4, CHRNA4, SERPINC1, C5, BCL2, DRD1, DRD2,
transcription factors (TFs) (Figure 4 and Table S6). DRD3, DRD4, COMT, MAOA, SLC6A3, SLC6A4, and
GABRA3. This refined gene set was subjected to clustering-
3.11. Clustering-enriched ontology across studies enriched ontology analysis using Metascape. 54
To extend the depth of our enrichment analyses, we Metascape first recognized all statistically enriched
utilized the systems biology-based meta-analysis and PGx terms, accumulative hypergeometric p-values, and
55
filtering. Variant Annotation Assessments were performed enrichment factors, which were computed and utilized
on each of the 27 candidate genes, revealing a total of 1,173 for filtering. Next, using a method akin to the NCI
PGx variants. Of these, 18 out of 27 genes had at least DAVID site (database for annotation, visualization and
one PGx variant and were included in the PGx-refined integrated discovery), the remaining relevant terms were
list. The goal of PGx filtering was to refine the gene list to hierarchically grouped into a tree according to Kappa-
pharmacogenes with established relevance to personalized statistical similarities based on gene memberships. A Kappa
medicine and potential therapeutic implications. The 18 similarity threshold of 0.3 was used to group the terms into
pharmacogenes include: APOE, TGFB1, OPRM1, ADH1B, clusters. Figure 5 displays a bar chart heatmap of the top
Volume 4 Issue 3 (2025) 5 doi: 10.36922/gpd.8090