Page 88 - GPD-4-3
P. 88
Gene & Protein in Disease Dopaminergic dysfunction as pre-addiction
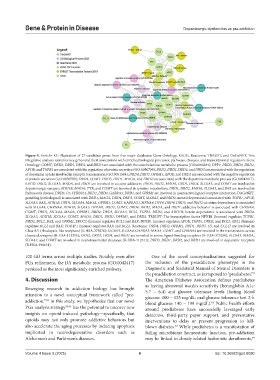
Figure 4. Enrichr-KG illustration of 27 candidate genes from five major databases: Gene Ontology, KEGG, Reactome, TRRUST, and DisGeNET. This
integrative analysis identifies key genes and their associations with enriched biological processes, pathways, diseases, and transcriptional regulators: Gene
Ontology: COMT, DRD2, DRD1, DRD3, and DRD4 are associated with the catecholamine metabolic process (GO:0006584); DPP4, DRD3, DRD4, DRD2,
APOE, and TGFB1 are associated with the regulation of protein secretion (GO:0050708); DRD2, DRD1, DRD4, and DRD3 are associated with the regulation
of dopamine uptake involved in synaptic transmission (GO:0051584); DRD4, DRD3, OPRM1, APOE, and DRD2 are associated with the negative regulation
of protein secretion (GO:0050709); DRD4, COMT, DRD3, DRD1, MAOA, and DRD2 are associated with the dopamine metabolic process (GO:0042417).
KEGG: DRD2, SLC6A3, MAOA, and DRD1 are involved in cocaine addiction; DRD3, DRD2, MAOA, DRD1, DRD4, SLC6A3, and COMT are involved in
dopaminergic synapse; ADH1B, MAOA, TYR, and COMT are involved in tyrosine metabolism; DRD1, DRD2, MAOA, SLC6A3, and BAX are involved in
Parkinson’s disease; DRD3, C5, CHRNA4, DRD2, DRD4, GABRA3, DRD1, and OPRM1 are involved in neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction. DisGeNET:
gambling (pathological) is associated with DRD1, MAOA, DRD4, DRD3, COMT, SLC6A3, and DRD2; mental depression is associated with TGFB1, APOE,
SLC6A3, BAX, ADH1B, DRD1, SLC6A4, MAOA, OPRM1, COMT, GABRA3, CHRNA4, DPP4, DRD4, DRD3, and DRD2; nicotine dependence is associated
with SLC6A4, CHRNA4, ADH1B, SLC6A3, OPRM1, DRD3, COMT, DRD4, DRD2, MAOA, and DRD1; addictive behavior is associated with CHRNA4,
COMT, DRD1, SLC6A4, MAOA, OPRM1, DRD4, DRD3, SLC6A3, BCL2, TGFB1, DRD2, and ADH1B; heroin dependence is associated with DRD4,
SLC6A3, ADH1B, SLC6A4, COMT, MAOA, DRD1, DRD3, OPRM1, and DRD2. TRRUST: The transcription factor NFKB1 (human) regulates TGFB1,
DRD2, BCL2, BAX, and OPRM1; ERCC2 (human) regulates BCL2 and BAX; NFKB1 (mouse) regulates APOE, TGFB1, DRD2, and BCL2; ABL1 (human)
regulates BCL2 and BAX; POU4F1 (mouse) regulates BAX and BCL2. Reactome: DRD4, DRD2, OPRM1, DRD1, DRD3, C5, and CCL17 are involved in
Class A/1 (rhodopsin-like receptors) (R-HSA-373076); SLC6A3, SLC6A4, GABRA3, MAOA, COMT, and CHRNA4 are involved in the transmission across
chemical synapses (R-HSA-112315); DRD2, DRD3, DRD4, and DRD1 are invovled in amine ligand-binding receptors (R-HSA-375280); SLC6A3, MAOA,
SLC6A4, and COMT are involved in neurotransmitter clearance (R-HSA-112311); DRD3, DRD1, DRD2, and DRD4 are involved in dopamine receptors
(R-HSA-390651).
100 GO terms across multiple studies. Notably, even after One of the novel conceptualizations suggested for
PGx refinement, the DA metabolic process (GO:0042417) the inclusion of the preaddiction phenotype in the
persisted as the most significantly enriched pathway. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders is
the preaddiction construct, as juxtaposed to “prediabetes.”
8
4. Discussion The American Diabetes Association defines prediabetes
as having abnormal insulin sensitivity (hemoglobin A1c:
Emerging research in addiction biology has brought 5.7 – 6.4) and glucose tolerance levels (fasting blood
attention to a novel conceptual framework called “pre- glucose: 100 – 125 mg/dL; oral glucose tolerance test 2-h
addiction.” In this study, we hypothesize that our novel blood glucose: 140 – 199 mg/dL). Public health efforts
5,8
62
PGx analysis strategy 54-61 has the potential to uncover new around prediabetes have successfully leveraged early
insights on opioid-induced pathology—specifically, that detection, third-party payor support, and preventative
opioids may not only promote addictive behaviors but interventions to delay or prevent progression to full-
also accelerate the aging processes by inducing apoptosis blown diabetes. While prediabetes is a manifestation of
63
implicated in neurodegenerative disorders such as failing microbiome homeostatic function, pre-addiction
Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases. may be linked to closely related hedonistic derailments,
64
Volume 4 Issue 3 (2025) 6 doi: 10.36922/gpd.8090