Page 99 - GPD-4-3
P. 99
Gene & Protein in Disease ABCA12 gene in Harlequin ichthyosis
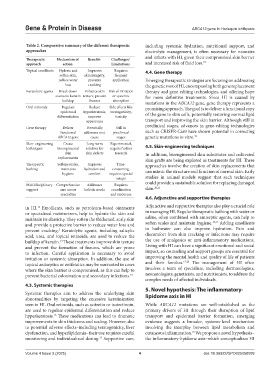
Table 2. Comparative summary of the different therapeutic including systemic hydration, nutritional support, and
approaches electrolyte management, is often necessary for neonates
and infants with HI, given their compromised skin barrier
Therapeutic Mechanism of Benefits Challenges/
approach action Limitations and increased risk of fluid loss. 18
Topical emollients Hydrate and Improves Requires 4.4. Gene therapy
soften skin, skin integrity, frequent
reduce water prevents application Emerging therapeutic strategies are focusing on addressing
loss cracking the genetic root of HI, encompassing both gene replacement
Keratolytic agents Break down Enhance skin Risk of irritation therapy and gene editing technologies, and offering hope
excessive keratin texture, prevent or systemic for more definitive treatments. Since HI is caused by
buildup fissures absorption mutations in the ABCA12 gene, gene therapy represents a
Oral retinoids Regulate Reduce Side effects like promising approach. The goal is to deliver a functional copy
epidermal hyperkeratosis, teratogenicity,
differentiation improve toxicity of the gene to skin cells, potentially restoring normal lipid
appearance transport and improving the skin barrier. Although still in
Gene therapy Deliver Potentially Still in preclinical stages, advances in gene-editing technologies
functional addresses root preclinical such as CRISPR-Cas9 have shown potential in correcting
ABCA12 gene cause stages genetic mutations in vitro. 19
Skin- engineering Create Long-term Experimental, 4.5. Skin-engineering techniques
techniques bioengineered solution for require further
skin skin defects research In addition, bioengineered skin substitutes and cultivated
replacements skin grafts are being explored as treatments for HI. These
Therapeutic Softens scales, Improves Time- approaches involve the creation of skin replacements that
bathing maintains hydration and consuming, can mimic the structure and function of normal skin. Early
hygiene comfort requires special
setups studies in animal models suggest that such techniques
Multidisciplinary Comprehensive Addresses Requires could provide a sustainable solution for replacing damaged
support care across holistic needs coordination skin. 20,21
specialties and resources
4.6. Adjunctive and supportive therapies
in HI. Emollients, such as petroleum-based ointments Adjunctive and supportive therapies also play a crucial role
12
or specialized moisturizers, help to hydrate the skin and in managing HI. Regular therapeutic bathing with water or
maintain its elasticity. They soften the thickened, scaly skin saline, often combined with antiseptic agents, can help to
and provide a protective barrier to reduce water loss and soften scales and maintain hygiene. 16,22 Adding emollients
prevent cracking. Keratolytic agents, including salicylic to bathwater can also improve hydration. Pain and
3
acid, urea, and topical retinoids, are used to reduce the discomfort from skin cracking or infections may require
buildup of keratin. These treatments improve skin texture the use of analgesics or anti-inflammatory medications.
14
and prevent the formation of fissures, which are prone Living with HI can have a significant emotional and social
to infection. Careful application is necessary to avoid impact, so counseling and support groups are essential for
irritation or systemic absorption. In addition, the use of improving the mental health and quality of life of patients
topical antiseptics or antibiotics may be warranted in cases and their families. 17,23 The management of HI often
where the skin barrier is compromised, as this can help to involves a team of specialists, including dermatologists,
prevent bacterial colonization and secondary infections. 15 neonatologists, geneticists, and nutritionists, to address the
complex needs of affected individuals.
4.3. Systemic therapies
5. Novel hypothesis: The inflammatory-
Systemic therapies aim to address the underlying skin lipidome axis in HI
abnormalities by targeting the excessive keratinization
seen in HI. Oral retinoids, such as acitretin or isotretinoin, While ABCA12 mutations are well-established as the
are used to regulate epidermal differentiation and reduce primary drivers of HI through their disruption of lipid
hyperkeratosis. These medications can lead to dramatic transport and epidermal barrier formation, emerging
16
improvements in skin thickness and scaling. However, due evidence suggests a broader, systems-level mechanism
to potential adverse effects–including teratogenicity, liver involving the interplay between lipid metabolism and
dysfunction, and hyperlipidemia–their use requires careful cutaneous inflammation. We propose a novel hypothesis–
18
monitoring and individualized dosing. Supportive care, the inflammatory-lipidome axis–which conceptualizes HI
17
Volume 4 Issue 3 (2025) 4 doi: 10.36922/GPD025050009