Page 106 - GTM-2-1
P. 106
Global Translational Medicine GalNAc AGT ASO reduce atherosclerosis
A
B
C D
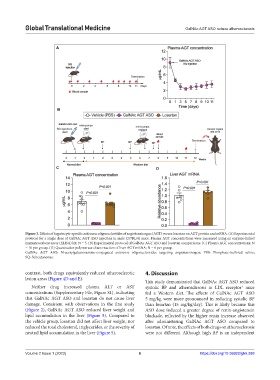
Figure 3. Effects of hepatocyte-specific antisense oligonucleotides of angiotensinogen (AGT) versus losartan on AGT protein and mRNA. (A) Experimental
protocol for a single dose of GalNAc AGT ASO injection in male C57BL/6J mice. Plasma AGT concentrations were measured using an enzyme-linked
immunosorbent assay (ELISA) kit; N = 5. (B) Experimental protocol of GalNAc AGT ASO and losartan comparisons. (C) Plasma AGT concentrations; N
= 10 per group. (D) Quantitative polymerase chain reaction of liver AGT mRNA; N = 6 per group.
GalNAc AGT ASO: N-acetylgalactosamine-conjugated antisense oligonucleotides targeting angiotensinogen; PBS: Phosphate-buffered saline;
SQ: Subcutaneous.
contrast, both drugs equivalently reduced atherosclerotic 4. Discussion
lesion areas (Figure 4D and E).
This study demonstrated that GalNAc AGT ASO reduced
Neither drug increased plasma ALT or AST systolic BP and atherosclerosis in LDL receptor mice
-/-
concentrations (Supplementary File, Figure S1), indicating fed a Western diet. The effects of GalNAc AGT ASO
that GalNAc AGT ASO and losartan do not cause liver 5 mg/kg were more pronounced in reducing systolic BP
damage. Consistent with observations in the first study than losartan (15 mg/kg/day). This is likely because this
(Figure 2), GalNAc AGT ASO reduced liver weight and ASO dose induced a greater degree of renin-angiotensin
lipid accumulation in the liver (Figure 5). Compared to blockade, reflected by the higher renin increase observed
the vehicle group, losartan did not affect liver weight, nor after administering GalNAc AGT ASO compared to
reduced the total cholesterol, triglycerides, or the severity of losartan. Of note, the effects of both drugs on atherosclerosis
neutral lipid accumulation in the liver (Figure 5). were not different. Although high BP is an independent
Volume 2 Issue 1 (2023) 6 https://doi.org/10.36922/gtm.288