Page 9 - GTM-2-1
P. 9
Global Translational Medicine Mineralocorticoid receptor in CMD
inflammatory factors, with no change in the recruitment of MR deficiency also inhibits the migration and proliferation
macrophages to the heart [37,38] . In an L-NAME/Ang II-induced of macrophages both in vivo and in vitro . However, further
[23]
hypertension model, MR deficiency in macrophages not only research is required to determine the underlying mechanism.
protects against cardiac hypertrophy, fibrosis, and vascular
damage, but also decreases macrophage recruitment to the 2.1.5. Role of macrophage MR in obesity and diabetes
heart . Intriguingly, in this model, the blood pressure of Macrophages are closely related to obesity and type 2
[22]
macrophage MR deficient mice was slightly elevated . diabetes mellitus (T2DM) . MR antagonists have been
[22]
[39]
Mechanistically, MR deficiency in macrophages inhibits shown to improve hepatic steatosis and insulin resistance
the expression of M1 markers and increases the expression in obese animal models [40,41] . A deficiency in macrophage
of alternatively activated M2 markers . In addition, MR MR improves glucose intolerance, insulin resistance,
[22]
deficiency synergizes with interleukin (IL)-4 to facilitate the and hepatic steatosis in obese mice , implying that
[42]
polarization of macrophages to M2 phenotype signaling macrophage MR plays an important role in obesity and
[22]
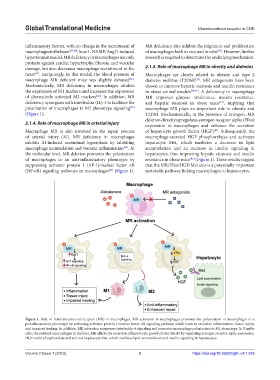
(Figure 1). T2DM. Mechanistically, in the presence of estrogen, MR
deletion directly upregulates estrogen receptor alpha (ERα)
2.1.4. Role of macrophage MR in arterial injury expression in macrophages and enhance the secretion
Macrophage MR is also involved in the repair process of hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) . Subsequently, the
[42]
of arterial injury (AI). MR deficiency in macrophages macrophage-secreted HGF phosphorylates and activates
inhibits AI-induced neointimal hyperplasia by inhibiting hepatocyte Met, which mediates a decrease in lipid
macrophage accumulation and vascular inflammation . At accumulation and an increase in insulin signaling in
[23]
the molecular level, MR deletion promotes the polarization hepatocytes, thus improving hepatic steatosis and insulin
of macrophages to an anti-inflammatory phenotype by resistance in obese mice (Figure 1). These results suggest
[42]
suppressing activator protein 1 (AP-1)/nuclear factor κB that the MR/ERα/HGF/Met axis is a potentially important
(NF-κB) signaling pathways in macrophages (Figure 1). metabolic pathway linking macrophages to hepatocytes.
[23]
Figure 1. Role of mineralocorticoid receptor (MR) in macrophages. MR activation in macrophages promotes the polarization of macrophages to a
proinflammatory phenotype by activating activator protein 1/nuclear factor κB signaling pathway, which leads to excessive inflammation, tissue injury,
and impaired healing. In addition, MR activation suppresses interleukin-4 signaling and promotes macrophage polarization to M1 phenotype. In Kupffer
cells, the resident macrophages in the liver, MR affects the secretion of hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) by regulating estrogen receptor alpha expression.
HGF could phosphorylate and activate hepatocyte Met, which mediates lipid accumulation and insulin signaling in hepatocytes.
Volume 2 Issue 1 (2023) 3 https://doi.org/10.36922/gtm.v2i1.229