Page 14 - GTM-2-1
P. 14
Global Translational Medicine Mineralocorticoid receptor in CMD
aldosterone promotes ECM production through the direct ablation can improve the recovery of cardiac systolic function
activation of fibroblasts remains a controversy. Fullerton and reduce arrhythmia post-ischemia/reperfusion [100] . The
et al. have shown that aldosterone has no direct effect on enhanced systolic function and decreased arrhythmia in
collagen synthesis in cultured rat cardiac fibroblasts . the heart of cardiomyocyte MR knockout mice have been
[95]
On the contrary, Brilla et al. have demonstrated that low found to be associated with decreased calcium/calmodulin-
concentration of aldosterone increases collagen synthesis dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII) activation and
in cultured cardiac fibroblasts, and the effect of aldosterone sodium-hydrogen exchanger-1 expression (NHE-1) [100]
can be inhibited by spironolactone . Previous animal (Figure 4). CaMKII is involved in pathophysiological
[96]
studies have shown that fibroblast-specific MR deficiency MR signaling in ischemic heart disease [101] . Moreover, the
has no effect on cardiac function, cardiac hypertrophy, inhibition of NHE-1 could suppress ventricular arrhythmia
and fibrosis following TAC . It has not been investigated in an ischemia-reperfusion model [102] . However, the ablation
[97]
whether fibroblast MR plays a role in other CVDs. of MR in myocytes does not affect the development of
cardiac hypertrophy, fibrosis, apoptosis, or inflammation in
4. Cardiomyocyte MR and CMDs TAC mouse model despite its protective effects on cardiac
[97]
4.1. Role of cardiomyocyte MR in MI and HF dilation and dysfunction .
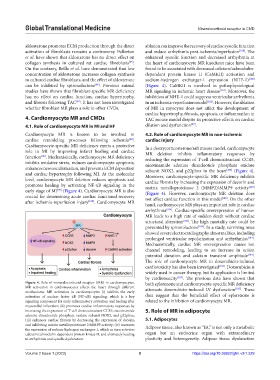
Cardiomyocyte MR is known to be involved in 4.2. Role of cardiomyocyte MR in non-ischemic
cardiac remodeling processes following ischemia . cardiac injury
[98]
Cardiomyocyte-specific MR deficiency exerts a protective In a deoxycorticosterone/salt mouse model, cardiomyocyte
role in MI by improving infarct healing and cardiac MR deletion inhibits inflammatory responses by
function . Mechanistically, cardiomyocyte MR deficiency reducing the expression of T-cell chemoattractant CCR5,
[99]
inhibits oxidative stress, reduces cardiomyocyte apoptosis, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase
enhances neovascularization, and prevents ECM deposition subunit NOX2, and p22phox in the heart [103] (Figure 4).
and cardiac hypertrophy following MI. At the molecular Moreover, cardiomyocyte-specific MR deficiency inhibits
level, cardiomyocyte MR deletion reduces apoptosis and cardiac fibrosis by increasing the expression of decorin and
promotes healing by activating NF-κB signaling in the matrix metalloproteinase 2 (MMP2)/MMP9 activity [103]
early stage of MI (Figure 4). Cardiomyocyte MR is also (Figure 4). However, cardiomyocyte MR deletion does
[99]
crucial for determining acute cardiac functional recovery not affect cardiac function in this model [103] . On the other
after ischemia-reperfusion injury [100] . Cardiomyocyte MR hand, cardiomyocyte MR plays an important role in cardiac
arrhythmia [104] . Cardiac-specific overexpression of human
MR leads to a high rate of sudden death without cardiac
structural alteration [104] . The high mortality rate could be
prevented by spironolactone [104] . In a study, surviving mice
showed severe electrocardiography abnormalities, including
prolonged ventricular repolarization and arrhythmias [104] .
Mechanistically, cardiac MR overexpression causes ion
channel remodeling, leading to an increase in action
potential duration and calcium transient amplitude [104] .
The role of cardiomyocyte MR in doxorubicin-induced
cardiotoxicity has also been investigated [105] . Doxorubicin is
widely used in cancer therapy, but its application is limited
by cardiotoxicity [105] . The previous data have shown that
Figure 4. Role of mineralocorticoid receptor (MR) in cardiomyocytes. both eplerenone and cardiomyocyte-specific MR deficiency
MR activation in cardiomyocytes affects the heart through different attenuate doxorubicin-induced LV dysfunction [105] . These
mechanisms. MR activation in cardiomyocytes (i) inhibits the early
activation of nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) signaling, which is a key data suggest that the beneficial effect of eplerenone is
signaling component for early inflammatory activation and healing after related to the inhibition of cardiomyocyte MR.
myocardial infarction; (ii) promotes cardiac inflammatory responses by
increasing the expression of T-cell chemoattractant CCR5, nicotinamide 5. Role of MR in adipocyte
adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase subunit NOX2, and p22phox;
(iii) enhances cardiac fibrosis by decreasing the expression of decorin 5.1. Adipocytes
and inhibiting matrix metalloproteinase 2/MMP9 activity; (iv) increases Adipose tissue, also known as “fat,” is not only a metabolic
the expression of sodium-hydrogen exchanger-1, which in turn activates
calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II, and ultimately leading organ but an endocrine organ with extraordinary
to arrhythmia and systolic dysfunction. plasticity and heterogeneity. Adipose tissue dysfunction
Volume 2 Issue 1 (2023) 8 https://doi.org/10.36922/gtm.v2i1.229