Page 91 - GTM-2-3
P. 91
Global Translational Medicine HPLC-UV lacosamide quantification
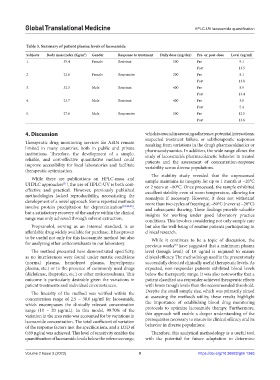
Table 3. Summary of patient plasma levels of lacosamide
Subjects Body mass index (Kg/m ) Gender Response to treatment Daily dose (mg/day) Pre‑ or post‑dose Level (ug/ml)
2
1. 35.4 Female Resistant 500 Pre 9.1
Post 13.5
2. 22.6 Female Responsive 200 Pre 8.1
Post 13.8
3. 32.3 Male Resistant 400 Pre 8.9
Post 13.4
4. 23.7 Male Resistant 400 Pre 3.6
Post 5.4
5. 27.6 Male Responsive 500 Pre 12.5
Post 13.6
4. Discussion which is crucial in assessing adherence, potential interactions,
suspected treatment failure, or subtherapeutic responses
Therapeutic drug monitoring services for AEDs remain resulting from variations in the drug’s pharmacokinetics or
limited in many countries, both in public and private pharmacodynamics. In addition, the wide range allows the
institutions. Therefore, the development of a simple, study of lacosamide’s pharmacokinetic behavior in treated
reliable, and cost-effective quantitative method could patients and the assessment of concentration-response
improve accessibility for local laboratories and facilitate variability across diverse populations.
therapeutic optimization.
The stability study revealed that the unprocessed
While there are publications on HPLC-mass and sample maintains its integrity for up to 1 month at −20°C
UHPLC approaches , the use of HPLC-UV is both cost- or 2 years at −80°C. Once processed, the sample exhibited
[21]
effective and practical. However, previously published excellent stability even at room temperature, allowing for
methodologies lacked reproducibility, necessitating the reanalysis if necessary. However, it does not withstand
development of a novel approach. Some reported methods more than two cycles of freezing at −80°C (never at −20°C)
involve protein precipitation for deproteinization [10,22,23] , and subsequent thawing. These findings provide valuable
but a satisfactory recovery of the analyte within the clinical insights for working under good laboratory practice
range was only achieved through solvent extraction.
conditions. This involves considering not only sample care
Propranolol, serving as an internal standard, is an but also the well-being of routine patients participating in
affordable drug widely available for purchase. It has proven clinical research.
to be useful not only for this lacosamide method but also While it continues to be a topic of discussion, the
for analyzing other anticonvulsants in our laboratory.
[5]
previous works have suggested that a minimum plasma
The method presented here demonstrated specificity, level (trough level) of 10 ug/ml is required to ensure
as no interferences were found under matrix conditions clinical efficacy. The methodology used in the present study
(normal plasma, hemolyzed plasma, hyperlipemic successfully detected clinically useful therapeutic levels. As
plasma, etc.) or in the presence of commonly used drugs expected, non-responder patients exhibited blood levels
(diclofenac, ibuprofen, etc.) or other anticonvulsants. This below the therapeutic range. It was also noteworthy that a
outcome is particularly desirable given the variations in patient classified as a responder achieved therapeutic effects
patient treatments and individual circumstances. with lower trough levels than the recommended threshold.
The linearity of the method was verified within the Despite the small sample size, which was primarily aimed
concentration range of 2.5 – 30.0 µg/ml for lacosamide, at assessing the method’s utility, these results highlight
which encompasses the clinically relevant concentration the importance of establishing blood drug monitoring
range (10 – 20 µg/mL). In this model, 99.70% of the protocols to optimize lacosamide therapy. Furthermore,
variation in the area ratio was accounted for by variations in this approach will enable a deeper understanding of the
lacosamide concentration. The total coefficient of variation prerequisites necessary to ensure its clinical efficacy and its
of the response factors met the specifications, and a LOD of behavior in diverse populations.
0.69 µg/ml was achieved. This level of sensitivity enables the Therefore, this analytical methodology is a useful tool
quantification of lacosamide levels below the reference range, with the potential for future adaptation to determine
Volume 2 Issue 3 (2023) 9 https://doi.org/10.36922/gtm.1265