Page 60 - GTM-3-3
P. 60
Global Translational Medicine COVID-19 and acute kidney injury
A B
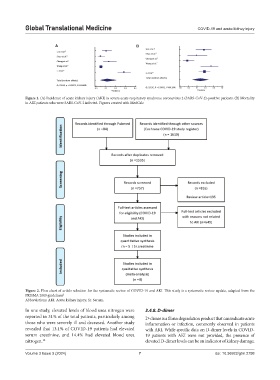
Figure 1. (A) Incidence of acute kidney injury (AKI) in severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2)-positive patients. (B) Mortality
in AKI patients who were SARS-CoV-2 infected. Figures created with MedCalc
Figure 2. Flow chart of article selection for the systematic review of COVID-19 and AKI. This study is a systematic review update, adapted from the
PRISMA 2009 guidelines 3
Abbreviations: AKI: Acute kidney injury; Sr: Serum.
In one study, elevated levels of blood urea nitrogen were 3.4.8. D-dimer
reported in 31% of the total patients, particularly among D-dimer is a fibrin degradation product that can indicate acute
those who were severely ill and deceased. Another study inflammation or infection, commonly observed in patients
revealed that 13.1% of COVID-19 patients had elevated with AKI. While specific data on D-dimer levels in COVID-
serum creatinine, and 14.4% had elevated blood urea 19 patients with AKI were not provided, the presence of
nitrogen. 12 elevated D-dimer levels can be an indicator of kidney damage.
Volume 3 Issue 3 (2024) 7 doi: 10.36922/gtm.2798