Page 57 - GTM-4-1
P. 57
Global Translational Medicine Incretins and cardiorenal disease
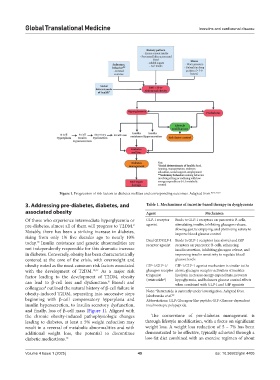
Figure 1. Progression of risk factors to diabetes mellitus and corresponding outcomes. Adapted from 10,16,17,18
3. Addressing pre-diabetes, diabetes, and Table 1. Mechanisms of incretin‑based therapy in dysglycemia
associated obesity Agent Mechanism
Of those who experience intermediate hyperglycemia or GLP-1 receptor Binds to GLP-1 receptors on pancreatic B-cells,
9
pre-diabetes, almost all of them will progress to T2DM. agonist stimulating insulin, inhibiting glucagon release,
Notably, there has been a striking increase in diabetes, slowing gastric emptying, and promoting satiety to
improve blood glucose control
rising from only 1% five decades ago to nearly 10% Dual GIP/GLP-1 Binds to GLP-1 receptors (see above) and GIP
10
today. Insulin resistance and genetic abnormalities are receptor agonist receptors on pancreatic B-cells, enhancing
not independently responsible for this dramatic increase insulin secretion, inhibiting glucagon release, and
in diabetes. Conversely, obesity has been characteristically improving insulin sensitivity to regulate blood
centered at the core of the crisis, with overweight and glucose levels
obesity noted as the most common risk factors associated GIP-1/GLP-1/ GIP-1/GLP-1 agonist mechanism is similar to the
with the development of T2DM. 10,11 As a major risk glucagon receptor above; glucagon receptor activation stimulates
factor leading to the development of T2DM, obesity triagonist lipolysis, increases energy expenditure, prevents
hypoglycemia, and balances glucose control effects
(retatrutide*)
8
can lead to β-cell loss and dysfunction. Biondi and when combined with GLP-1 and GIP agonists
colleagues outlined the natural history of β-cell failure in Note: *Retatrutide is currently under investigation. Adapted from
8
obesity-induced T2DM, separating into successive steps Jakubowska et al. 20
beginning with β-cell compensatory hyperplasia and Abbreviations: GLP: Glucagon-like peptide; GIP: Glucose-dependent
insulin hypersecretion, to insulin secretory dysfunction, insulinotropic polypeptide.
and finally, loss of β-cell mass (Figure 1). Aligned with
the chronic obesity-induced pathophysiologic changes The cornerstone of pre-diabetes management is
leading to diabetes, at least a 5% weight reduction may through lifestyle modification, with a focus on significant
result in a reversal of metabolic abnormalities and with weight loss. A weight loss reduction of 5 – 7% has been
additional weight loss, the potential to discontinue demonstrated to be effective, typically achieved through a
diabetic medications. 12 low-fat diet combined with an exercise regimen of about
Volume 4 Issue 1 (2025) 49 doi: 10.36922/gtm.4405