Page 51 - GTM-4-2
P. 51
Global Translational Medicine SPION for cancer theranostics
A
B
C
D
E F G
H I J
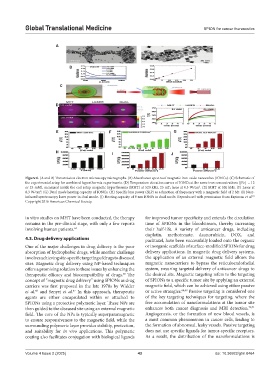
Figure 6. (A and B) Transmission electron microscopy micrographs. (B) Absorbance spectra of magnetic iron oxide nanocubes (IONCs). (C) Schematic of
the experimental setup for combined hyperthermia experiments. (D) Temperature elevation curves of IONCs at the same iron concentrations ([Fe] = 12
or 25 mM), measured inside the coil setup magnetic hyperthermia (MHT) at 520 kHz, 25 mT; laser at 0.3 W/cm . (E) MHT at 520 kHz. (F) Laser at
2
0.3 W/cm . (G) Dual mode heating capacity of IONCs. (H) Specific loss power (SLP) as a function of frequency with a magnetic field of 2 Mt. (I) Near-
2
infrared spectroscopy laser power in dual mode. (J) Heating capacity of 9 nm IONPs in dual mode. Reproduced with permission from Espinosa et al.
61
Copyright 2016 American Chemical Society.
in vitro studies on MHT have been conducted, the therapy for improved tumor specificity and extends the circulation
remains in the pre-clinical stage, with only a few reports time of SPIONs in the bloodstream, thereby increasing
involving human patients. 64 their half-life. A variety of anticancer drugs, including
cisplatin, methotrexate, daunorubicin, DOX, and
4.3. Drug delivery applications paclitaxel, have been successfully loaded onto the organic
One of the major challenges in drug delivery is the poor or inorganic scaffolds of surface-modified SPIONs for drug
absorption of hydrophobic drugs, while another challenge delivery applications. In magnetic drug delivery systems,
involves achieving site-specific targeting of drugs to diseased the application of an external magnetic field allows the
sites. Magnetic drug delivery using NP-based techniques magnetic nanocarriers to bypass the reticuloendothelial
offers a promising solution to these issues by enhancing the system, ensuring targeted delivery of anticancer drugs to
therapeutic efficacy and biocompatibility of drugs. The the desired site. Magnetic targeting refers to the targeting
65
concept of “magnetic drug delivery” using SPIONs as drug of SPIONs to a specific tumor site by applying an external
carriers was first proposed in the late 1970s by Widder magnetic field, which can be achieved using either passive
et al. and Senyei et al. In this approach, therapeutic or active strategies. 68,69 Passive targeting is considered one
67
66
agents are either encapsulated within or attached to of the key targeting techniques for targeting, where the
SPIONs using a protective polymeric layer. These NPs are free accumulation of nanoformulations at the tumor site
then guided to the diseased site using an external magnetic enhances both cancer diagnosis and MRI detection. 70,71
field. The core of the NPs is typically superparamagnetic Angiogenesis, or the formation of new blood vessels, is
to ensure responsiveness to the magnetic field, while the a most common phenomenon in cancer cells, leading to
surrounding polymeric layer provides stability, protection, the formation of abnormal, leaky vessels. Passive targeting
and suitability for in vivo applications. This polymeric does not use specific ligands for tumor-specific receptors.
coating also facilitates conjugation with biological ligands As a result, the distribution of the nanoformulations is
Volume 4 Issue 2 (2025) 43 doi: 10.36922/gtm.8464