Page 47 - GTM-4-2
P. 47
Global Translational Medicine SPION for cancer theranostics
properties of Au and SPIONs, which can affect the long- including as contrast agents in MRI, magnetic fluid
term stability and consistency of the Au shell. 31,32 hyperthermia agents, and drug delivery systems. Their
The integration of SPIONs with Ag offers several unique magnetic properties enable a wide range of
advantages. By combining SPIONs with Ag NPs or applications in both diagnostics and therapeutics, making
an Ag shell, these coatings can be functionalized with them a cornerstone of modern biomedical research and
clinical practices. This section provides a detailed
7,23
biomolecules to improve cell interactions. In addition, explanation of these approaches, along with their current
the antimicrobial properties of Ag can be beneficial for limitations and recent developments.
cancer therapy with antimicrobial effects. However, the
Ag coating can reduce the magnetic properties of SPIONs, 4.1. MRI
which may diminish MRI contrast. Ag toxicity at high Significant advancements have been made in medical
doses and stability issues further limit their biomedical imaging technology for disease diagnosis with the
applications. A comparison of different types of coatings introduction of non-invasive techniques such as MRI. 33,34
with SPIONs and their stability in biological environments The use of SPIONs as contrast agents for MRI applications
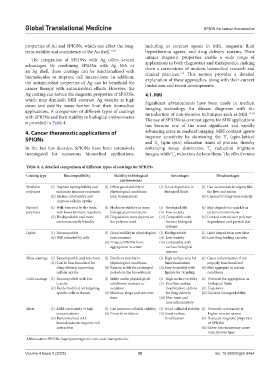
is provided in Table 4.
has become one of the most significant and rapidly
4. Cancer theranostic applications of advancing areas in medical imaging. MRI contrast agents
SPIONs improve sensitivity by shortening the T (spin-lattice)
1
and T (spin-spin) relaxation times of protons, thereby
2
In the last few decades, SPIONs have been extensively enhancing tissue distinction. T reduction brightens
1
investigated for numerous biomedical applications, images, while T reduction darkens them. The effectiveness
2
Table 4. A detailed comparison of different types of coatings for SPIONs
Coating type Biocompatibility Stability in biological Advantages Disadvantages
environments
Synthetic (i) Improve hydrophilicity and (i) Offers good stability in (i) Good dispersion in (i) Can accumulate in organs like
polymers minimize immune responses physiological conditions biological fluids the liver and spleen
(ii) Reduce cytotoxicity and (pH, temperature) (ii) Can lead to long-term toxicity
improve cellular uptake
Natural (i) Well-tolerated by the body, (i) Moderate stability in some (i) Biodegradable (i) May degrade too quickly in
polymers with lower immune reactions. biological environments (ii) Low toxicity certain environments
(ii) Biodegradable and more (ii) Degradation rates depend on (iii) Compatible with (ii) Limited control over polymer
environmentally friendly the polymer used various biological degradation and particle size
systems
Lipids (i) Biocompatible (i) Good stability in physiological (i) Biodegradable (i) Lipid degradation over time
(ii) Well tolerated by cells environments (ii) Low toxicity (ii) Low drug loading capacity
(ii) Protects SPIONs from (iii) Compatible with
aggregation in serum various biological
systems
Silica coatings (i) Biocompatible and non-toxic (i) Excellent stability in (i) High surface area for (i) Cause inflammation if not
(ii) Can be functionalized for physiological conditions functionalization properly functionalized
drug delivery, improving (ii) Remain stable for prolonged (ii) Easy to modify with (ii) May aggregate in certain
cellular uptake periods in the bloodstream ligands for targeting conditions
Gold coatings (i) Biocompatible with low (i) Stable under physiological (i) High surface stability (i) Potential for aggregation in
toxicity conditions, resistant to (ii) Excellent surface biological fluids
(ii) Easily modified for targeting oxidation modification options (ii) Expensive
specific cells or tissues (ii) Maintain shape and size over for drug delivery (iii) Limited biodegradability
time (iii) Non-toxic and
non-inflammatory
Silver (i) Mild cytotoxicity at high (i) Can improve colloidal stability (i) Good colloidal stability (i) Potential cytotoxicity at
concentrations (ii) Prone to oxidation (ii) Good surface higher concentrations
(ii) Functionalized with modification (ii) Reduced magnetic properties
biomolecules to improve cell of SPIONs
interaction (iii) Silver ion release may cause
toxicity over time
Abbreviation: SPIONs: Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles.
Volume 4 Issue 2 (2025) 39 doi: 10.36922/gtm.8464