Page 42 - GTM-4-2
P. 42
Global Translational Medicine SPION for cancer theranostics
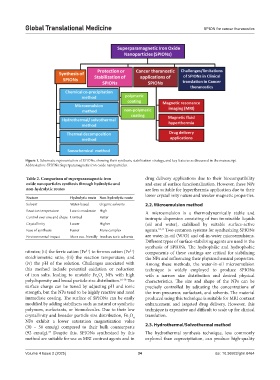
Figure 1. Schematic representation of SPIONs, showing their synthesis, stabilization strategy, and key features as discussed in the manuscript
Abbreviation: SPIONs: Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles.
Table 2. Comparison of superparamagnetic iron drug delivery applications due to their biocompatibility
oxide nanoparticles synthesis through hydrolytic and and ease of surface functionalization. However, these NPs
non‑hydrolytic routes are less suitable for hyperthermia application due to their
lower crystallinity nature and weaker magnetic properties.
Feature Hydrolytic route Non‑hydrolytic route
Solvent Water-based Organic solvents 2.2. Microemulsion method
Reaction temperature Low to moderate High A microemulsion is a thermodynamically stable and
Control over size and shape Limited Better isotropic dispersion consisting of two immiscible liquids
Crystallinity Lower Higher (oil and water), stabilized by suitable surface-active
Ease of synthesis Easier More complex agents. 16,17 Two common systems for synthesizing SPIONs
Environmental impact More eco-friendly Involves toxic solvents are water-in-oil (W/O) and oil-in-water microemulsions.
Different types of surface-stabilizing agents are used in the
synthesis of SPIONs. The hydrophilic and hydrophobic
nitrates; (ii) the ferric cation (Fe ) to ferrous cation (Fe ) components of these coatings are critical for stabilizing
3+
2+
stoichiometric ratio; (iii) the reaction temperature; and the NPs and influencing their physicochemical properties.
(iv) the pH of the solution. Challenges associated with Among these methods, the water-in-oil microemulsion
this method include potential oxidation or reduction technique is widely employed to produce SPIONs
of iron salts, leading to unstable Fe O NPs with high with a narrow size distribution and desired physical
4
3
polydispersity and broad particle size distribution. 16-18 The characteristics. The size and shape of the NPs can be
surface charge can be tuned by adjusting pH and ionic precisely controlled by adjusting the concentrations of
strength, but the NPs tend to be highly reactive and need the iron precursor, surfactant, and solvents. The material
immediate coating. The surface of SPIONs can be easily produced using this technique is suitable for MRI contrast
modified by adding stabilizers such as natural or synthetic enhancement and targeted drug delivery. However, this
polymers, surfactants, or biomolecules. Due to their low technique is expensive and difficult to scale up for clinical
crystallinity and broader particle size distribution, Fe O translation.
3
4
NPs exhibit a lower saturation magnetization value
(30 – 50 emu/g) compared to their bulk counterparts 2.3. Hydrothermal/Solvothermal method
(92 emu/g). Despite this, SPIONs synthesized by this The hydrothermal synthesis technique, less commonly
17
method are suitable for use as MRI contrast agents and in explored than coprecipitation, can produce high-quality
Volume 4 Issue 2 (2025) 34 doi: 10.36922/gtm.8464