Page 11 - GTM-4-3
P. 11
Global Translational Medicine Inflammation in CVD: Mechanisms and markers
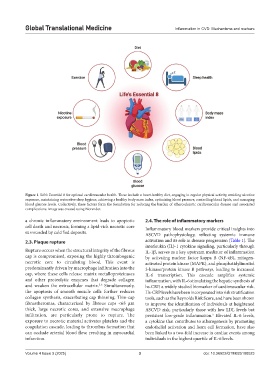
Figure 1. Life’s Essential 8 for optimal cardiovascular health. These include a heart-healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, avoiding nicotine
exposure, maintaining restorative sleep hygiene, achieving a healthy body mass index, optimizing blood pressure, controlling blood lipids, and managing
blood glucose levels. Collectively, these factors form the foundation for reducing the burden of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease and associated
complications. Image was created using Biorender.
a chronic inflammatory environment leads to apoptotic 2.4. The role of inflammatory markers
cell death and necrosis, forming a lipid-rich necrotic core Inflammatory blood markers provide critical insights into
surrounded by calcified deposits. ASCVD pathophysiology, reflecting systemic immune
2.3. Plaque rupture activation and its role in disease progression (Table 1). The
interleukin (IL)-1 cytokine signaling, particularly through
Rupture occurs when the structural integrity of the fibrous IL-1β, serves as a key upstream mediator of inflammation
cap is compromised, exposing the highly thrombogenic by activating nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB), mitogen-
necrotic core to circulating blood. This event is activated protein kinase (MAPK), and phosphatidylinositol
predominantly driven by macrophage infiltration into the 3-kinase/protein kinase B pathways, leading to increased
cap, where these cells release matrix metalloproteinases IL-6 transcription. This cascade amplifies systemic
and other proteolytic enzymes that degrade collagen inflammation, with IL-6 stimulating the hepatic synthesis of
and weaken the extracellular matrix. Simultaneously, hs-CRP, a widely studied biomarker of cardiovascular risk.
5,6
the apoptosis of smooth muscle cells further reduces Hs-CRP levels have been incorporated into risk stratification
collagen synthesis, exacerbating cap thinning. Thin-cap tools, such as the Reynolds Risk Score, and have been shown
fibroatheromas, characterized by fibrous caps <65 μm to improve the identification of individuals at heightened
thick, large necrotic cores, and extensive macrophage ASCVD risk, particularly those with low LDL levels but
infiltration, are particularly prone to rupture. The persistent low-grade inflammation. Elevated IL-6 levels,
5
exposure to necrotic material activates platelets and the a cytokine that contributes to atherogenesis by promoting
coagulation cascade, leading to thrombus formation that endothelial activation and foam cell formation, have also
can occlude arterial blood flow, resulting in myocardial been linked to a two-fold increase in cardiac events among
infarction. individuals in the highest quartile of IL-6 levels.
Volume 4 Issue 3 (2025) 3 doi: 10.36922/GTM025100023