Page 15 - GTM-4-3
P. 15
Global Translational Medicine Inflammation in CVD: Mechanisms and markers
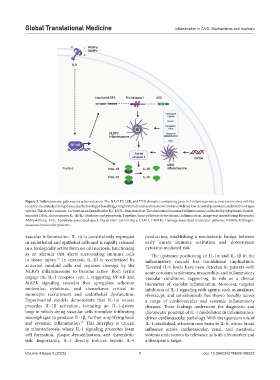
Figure 3. Inflammasome pathways in atherosclerosis. The NACHT, LRR, and PYD domains-containing protein 3 inflammasome activation involves toll-like
receptor-mediated priming via nuclear factor-kappa B and triggering by stimuli such as cholesterol crystals, oxidized low-density lipoprotein, and reactive oxygen
species. This leads to caspase-1 activation and interleukin (IL)-1β/IL-18 maturation. The absent in melanoma 2 inflammasome, activated by cytoplasmic double-
stranded DNA, also promotes IL-1β/IL-18 release and pyroptosis. Together, these pathways drive chronic inflammation. Image was created using Biorender.
Abbreviations: ASC: Apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a CARD; DAMPs: Damage-associated molecular patterns; PAMPs: Pathogen-
associated molecular patterns.
vascular inflammation. IL-1α is constitutively expressed production, establishing a mechanistic bridge between
in endothelial and epithelial cells and is rapidly released early innate immune activation and downstream
in a biologically active form on cell necrosis, functioning cytokine-mediated risk.
as an alarmin that alerts surrounding immune cells The upstream positioning of IL-1α and IL-1β in the
to tissue injury. In contrast, IL-1β is synthesized by inflammatory cascade has translational implications.
15
activated myeloid cells and requires cleavage by the Elevated IL-1 levels have been detected in patients with
NLRP3 inflammasome to become active. Both forms acute coronary syndromes, myocarditis, and inflammatory
engage the IL-1 receptor type 1, triggering NF-κB and vascular conditions, supporting its role as a clinical
MAPK signaling cascades that upregulate adhesion biomarker of vascular inflammation. Moreover, targeted
molecules, cytokines, and chemokines critical to inhibition of IL-1 signaling with agents, such as anakinra,
monocyte recruitment and endothelial dysfunction. rilonacept, and canakinumab, has shown benefits across
Experimental models demonstrate that IL-1α release a range of cardiovascular and systemic inflammatory
precedes IL-1β activation, initiating an IL-1-driven diseases. These findings underscore the diagnostic and
loop in which dying vascular cells stimulate infiltrating therapeutic potential of IL-1 modulation in inflammation-
macrophages to produce IL-1β, further amplifying local driven cardiovascular pathology. With the upstream role of
and systemic inflammation. This interplay is crucial IL-1 established, attention now turns to IL-6, whose broad
15
in atherosclerosis, where IL-1 signaling promotes foam influence across cardiovascular, renal, and metabolic
cell formation, plaque destabilization, and thrombotic systems underscores its relevance as both a biomarker and
risk. Importantly, IL-1 directly induces hepatic IL-6 a therapeutic target.
Volume 4 Issue 3 (2025) 7 doi: 10.36922/GTM025100023