Page 18 - IJAMD-1-2
P. 18
International Journal of AI for
Materials and Design
Sustainable electronics using AI/ML
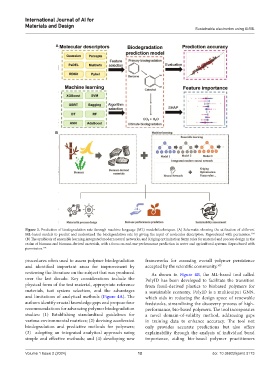
A
B
Figure 3. Prediction of biodegradation rate through machine language (ML) models/techniques. (A) Schematic showing the utilization of different
ML-based models to predict and understand the biodegradation rate by giving the input of molecular descriptors. Reproduced with permission.
104
(B) The symbiosis of ensemble learning, integrated modern neural networks, and Kriging optimization fuzzy rules for material and process design in the
realm of biomass and biomass-derived materials, with a focus on end-use performance prediction in water and agricultural systems. Reproduced with
permission. 105
procedures often used to assess polymer biodegradation frameworks for assessing overall polymer persistence
and identified important areas for improvement by accepted by the scientific community. 105
reviewing the literature on the subject that was produced As shown in Figure 4B, the ML-based tool called
over the last decade. Key considerations include the PolyID has been developed to facilitate the transition
physical form of the test material, appropriate reference from fossil-derived plastics to biobased polymers for
materials, test system selection, and the advantages a sustainable economy. PolyID is a multioutput GNN,
and limitations of analytical methods (Figure 4A). The which aids in reducing the design space of renewable
authors identify crucial knowledge gaps and propose four feedstocks, streamlining the discovery process of high-
recommendations for advancing polymer biodegradation performance, bio-based polymers. The tool incorporates
studies: (1) Establishing standardized guidelines for a novel domain-of-validity method, addressing gaps
various environmental matrices; (2) devising accelerated in training data to enhance accuracy. The tool not
biodegradation and predictive methods for polymers; only provides accurate predictions but also offers
(3) adopting an integrated analytical approach using explainability through the analysis of individual bond
simple and effective methods; and (4) developing new importance, aiding bio-based polymer practitioners
Volume 1 Issue 2 (2024) 12 doi: 10.36922/ijamd.3173