Page 35 - IJAMD-1-2
P. 35
International Journal of AI for
Materials and Design
AI-driven quality assurance in AM
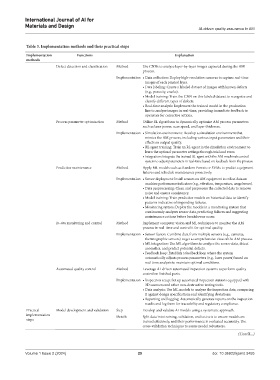
Table 3. Implementation methods and their practical steps
Implementation Functions Explanation
methods
Defect detection and classification Method Use CNNs to analyze layer-by-layer images captured during the AM
process.
Implementation • Data collection: Deploy high‑resolution cameras to capture real‑time
images of each printed layer.
• Data labeling: Create a labeled dataset of images with known defects
(e.g., porosity, cracks).
• Model training: Train the CNN on this labeled dataset to recognize and
classify different types of defects.
• Real‑time analysis: Implement the trained model in the production
line to analyze images in real-time, providing immediate feedback to
operators for corrective actions.
Process parameter optimization Method Utilize RL algorithms to dynamically optimize AM process parameters
such as laser power, scan speed, and layer thickness.
Implementation • Simulation environment: Develop a simulation environment that
mimics the AM process, including various input parameters and their
effects on output quality.
• RL agent training: Train an RL agent in the simulation environment to
learn the optimal parameter settings through trial and error.
• Integration: Integrate the trained RL agent with the AM machine’s control
system to adjust parameters in real-time based on feedback from the process.
Predictive maintenance Method Apply ML models such as Random Forests or SVMs to predict equipment
failures and schedule maintenance proactively.
Implementation • Sensor deployment: Install sensors on AM equipment to collect data on
machine performance indicators (e.g., vibration, temperature, usage hours).
• Data preprocessing: Clean and preprocess the collected data to remove
noise and ensure consistency.
• Model training: Train predictive models on historical data to identify
patterns indicative of impending failures.
• Monitoring system: Deploy the models in a monitoring system that
continuously analyzes sensor data, predicting failures and suggesting
maintenance actions before breakdowns occur.
In-situ monitoring and control Method Implement computer vision and ML techniques to monitor the AM
process in real-time and control it for optimal quality.
Implementation • Sensor fusion: Combine data from multiple sensors (e.g., cameras,
thermographic sensors) to get a comprehensive view of the AM process.
• ML integration: Use ML algorithms to analyze the sensor data, detect
anomalies, and predict potential defects.
• Feedback loop: Establish a feedback loop where the system
automatically adjusts process parameters (e.g., laser power) based on
real-time analysis to maintain optimal conditions.
Automated quality control Method Leverage AI-driven automated inspection systems to perform quality
control on finished parts.
Implementation • Inspection setup: Set up automated inspection stations equipped with
3D scanners and other non-destructive testing tools.
• Data analysis: Use ML models to analyze the inspection data, comparing
it against design specifications and identifying deviations.
• Reporting and logging: Automatically generate reports on the inspection
results and log them for traceability and regulatory compliance.
Practical Model development and validation Step Develop and validate AI models using a systematic approach.
implementation Details Split data into training, validation, and test sets to ensure models are
steps trained effectively, and their performance is evaluated accurately. Use
cross-validation techniques to assess model robustness.
(Cont’d...)
Volume 1 Issue 2 (2024) 29 doi: 10.36922/ijamd.3455