Page 190 - IJB-10-1
P. 190
International Journal of Bioprinting Nanoclay biopolymer inks for 3D printing
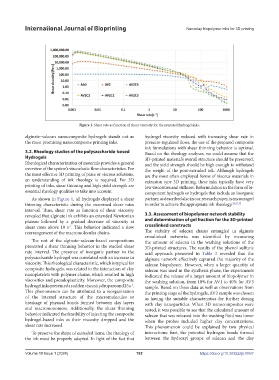
Figure 1. Shear rate as function of shear viscosity for the prepared hydrogel inks.
alginate–salecan nanocomposite hydrogels stands out as hydrogel viscosity reduced with increasing shear rate in
the most promising nanocomposite printing inks. pressure-regulated flows, the use of the prepared composite
ink formulations with shear thinning behavior is optimal.
3.2. Rheology studies of the polysaccharide-based Based on the rheology analyses, we could assume that the
Hydrogels 3D-printed material’s overall structure should be preserved,
Rheological characterization of materials provides a general and the yield strength should be high enough to withstand
overview of the system’s viscoelastic flow characteristics. For the weight of the post-extruded ink. Although hydrogels
the most effective 3D printing of paste or viscous solutions, are the most often employed forms of viscous materials in
an understanding of ink rheology is required. For 3D extrusion type 3D printing, these inks typically have very
printing of inks, shear thinning and high yield strength are low viscosities and stiffness. Reformulation in the form of bi-
essential rheology qualities to take into account. component hydrogels or hydrogels that include an inorganic
As shown in Figure 1, all hydrogels displayed a shear partner, as described also in our research paper, is encouraged
thinning characteristic during the examined shear rates in order to achieve the appropriate ink rheology. 24,25,53
interval. Thus, shear rate as function of shear viscosity
revealed that alginate ink exhibits an extended Newtonian 3.3. Assessment of biopolymer network stability
plateau followed by a gradual decrease of viscosity at and determination of gel fraction for the 3D-printed
shear rates above 10 s . This behavior indicated a slow crosslinked constructs
-1
rearrangement of the macromolecular chains. The stability of salecan chains entangled in alginate
crosslinked networks was identified by measuring
The rest of the alginate–salecan-based compositions the amount of salecan in the washing solutions of the
presented a shear thinning behavior in the studied shear 3D-printed structures. The results of the phenol sulfuric
rate interval. The presence of inorganic partner in the acid approach presented in Table 3 revealed that the
polysaccharide hydrogel was correlated with an increase in alginate network effectively captured the majority of the
viscosity. This rheological characteristic, which is typical for salecan biopolymer. However, when a larger quantity of
composite hydrogels, was related to the interaction of clay salecan was used in the synthesis phase, the experiments
nanoplatelets with polymer chains, which resulted in high indicated the release of a larger amount of biopolymer in
viscosities and pseudoplasticity. Moreover, the composite the washing solution, from 10% for AV1 to 40% for AV3
hydrogel inks presented a sudden viscosity drop around 25 s . sample. Based on these data as well as observations from
-1
This phenomenon can be attributed to a reorganization the printing stage of the hydrogels, AV2 sample was chosen
of the internal structure of the macromolecules or as having the suitable characteristics for further dosing
breakage of physical bonds formed between clay layers with clay nanoparticles. When 3D nanocomposites were
and macromonomers. Additionally, the shear thinning tested, it was possible to see that the calculated amount of
behavior indicated the feasibility of injecting the composite salecan that was released into the washing fluid was lower
hydrogel-based inks as their viscosity dropped and the when the probes included higher clay concentrations.
shear rate increased. This phenomenon could be explained by two physical
To preserve the shape of extruded items, the rheology of interactions: first, the potential hydrogen bonds formed
the ink must be properly adapted. In light of the fact that between the hydroxyl groups of salecan and the clay
Volume 10 Issue 1 (2024) 182 https://doi.org/10.36922/ijb.0967